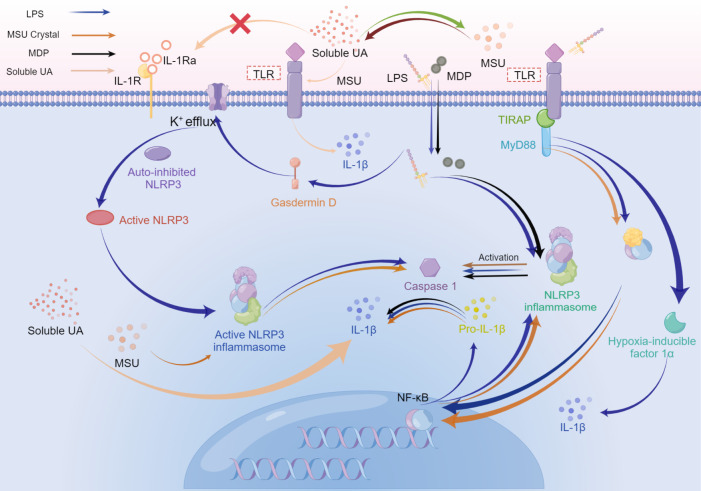
Figure 4.
The possible superposition of bacterial inflammation in periodontitis and sterile inflammation in hyperuricemia or gout when the above diseases coexist. Activation of Toll-like receptors, especially Toll-like receptor 4, switches metabolism from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis in immune cells, which increases HIF-α, and enhances IL-1β production. During the late phase of the NF-κB pathway stimulated by LPS, the final effect is the upregulation of pro-resolution cytokines. LPS, MDP, and MSU initiate the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome, activating caspase-1, which cleaves pro-IL-1β into mature IL-1β. While the production of NLRP3 is related to the MyD88-dependent pathway. Besides, IL-1β could be promoted by simultaneous stimulation from soluble UA and MSU crystals or MSU crystals solely. Soluble UA decreases the IL-1Ra, without assistance from other stimuli. LPS activates gasdermin D, resulting in K+ efflux. Subsequent assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome drives the activated caspase-1 cleave pro-IL-1β into IL-1β. Caspase-1, in turn, could stimulate gasdermin D to accelerate K+ efflux, accompanying the release of IL-1β.