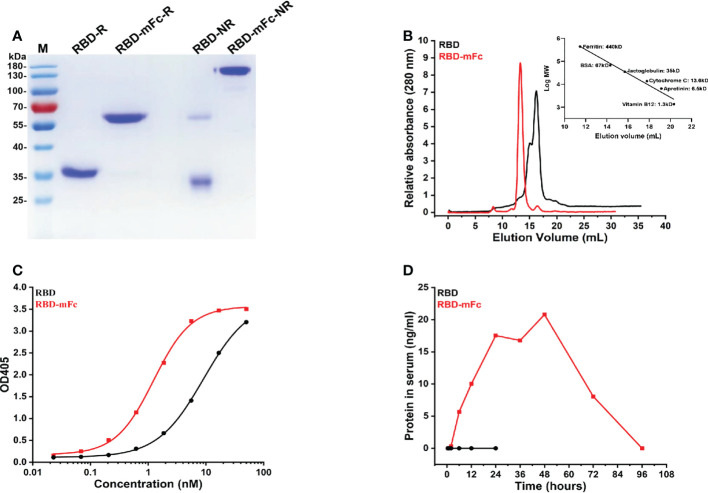
Figure 1.
RBD-mFc fusion protein is dimeric, functional and long-lasting in serum. (A) Analysis of RBD-mFc and RBD protein (approximately 4 μg each) under reducing and nonreducing conditions through SDS–PAGE (4-12% gradient gel) which indicated that RBD-mFc existed as a disulfide-linked dimer while RBD is a mixture of monomer and dimer. M, marker; R, reduced form; NR, nonreduced form. (B) Analysis of RBD-mFc and RBD proteins by size exclusion chromatography on Superdex 200 10/300 (GE). X-axis: elution volume (mL), Y-axis: A280 nm (a.u.) The right inset shows the standard curve. Two peaks were observed in the eluted RBD, while only one peak was separated from the eluted RBD-mFc, indicating that RBD-mFc was uniform. (C) Binding of RBD-mFc and RBD to hACE2-Fc, as measured by ELISA. The EC50 values of hACE2-Fc binding to coated RBD-mFc and RBD were estimated at 1.2 nM and 9.1 nM, respectively. Data are average values of two replicates. (D) Plasma half-life of RBD-mFc and RBD via intranasal administration. Purified RBD-mFc and RBD proteins (50 μg) were intranasally inoculated into BALB/c mice (n=3). Serum was collected at the times indicated on the abscissa. The protein concentration in pooled blood circulation were measured by ELISA. Substantial RBD-mFc accumulation and persistence in sera were observed while RBD was barely detectable.