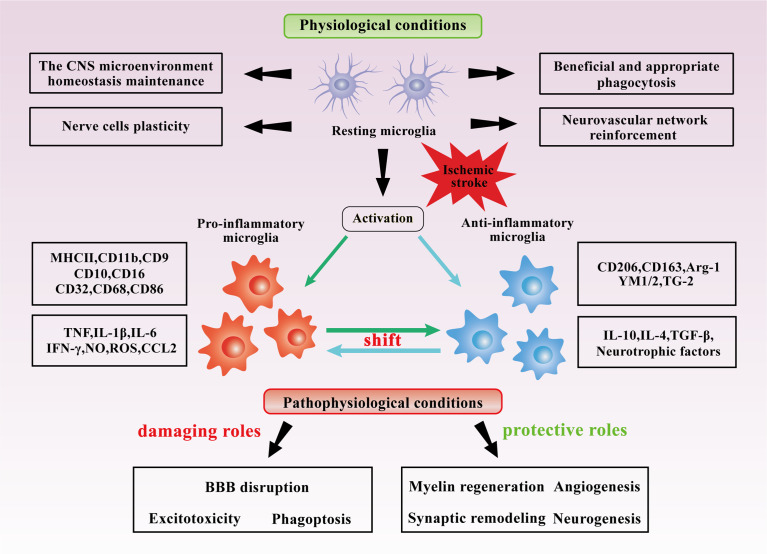
Figure 2.
Dual roles of microglia in IS. Under normal conditions, microglia maintain the CNS microenvironment homeostasis and appropriately regulate the neurovascular network. Under the stimulation of cerebral ischemia, microglia are likely to be primarily activated to anti-inflammatory states at the early stages and pro-inflammatory states at the later stages, synthesize and secrete various cytokines and mediators. In IS, Microglia may be beneficial in angiogenesis, myelin regeneration, synaptic remodeling, and neurogenesis in IS, but they may also be detrimental in BBB disruption, excitotoxicity, and phagoptosis.