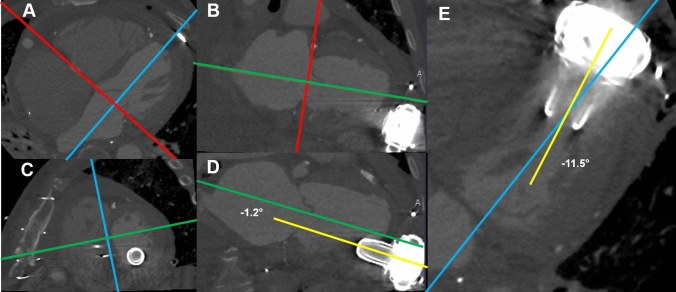
Fig. 1.
Example of Computed Tomography measurements. Computed tomography data were used to measure the implantation angle of the inflow cannula of the LVAD. Using a 3-dimensional MPR the LV long axis was reconstructed. A On a transversal plane, the MPR crosshair is aligned with the mitral valve annulus and the perpendicular part of the crosshair parallel to the LV long-axis. B This is repeated in the sagittal view to create a double oblique short-axis view of the LV. C The crosshair is further aligned to the septum to create a double oblique four-chamber and two-chamber view, with the crosshair parallel to the LV long-axis. (D + E) By adjusting the window settings the angle between the inflow cannula of the LVAD and the LV-axis can be visualized in the two-chamber (D; anterior or inferior) and four-chamber (E; septal or lateral) view. LV left ventricle, LVAD left ventricular assist device, MPR multiplanar reformation, PT pump thrombosis