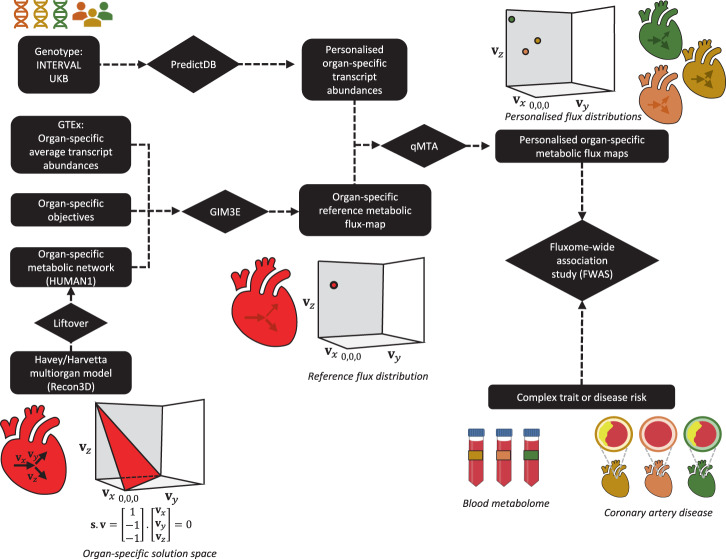
Fig. 1. Framework for computing organ-specific personalised genome-scale flux maps from genotype data and performing fluxome-wide association study (FWAS).
First, we extract the organ-subnetworks from the Harvey/Harvetta multiorgan models, which were built from Recon3D, and we perform a liftover to update them to HUMAN1, the most recent human GSMM. Then, a reference flux map is computed for each organ using the GIM3E algorithm to integrate average transcript abundances and organ-specific metabolic objectives into the organ-specific metabolic subnetwork. In parallel, personalised organ-specific transcript abundances are imputed from genotype data of the INTERVAL and UK Biobank (UKB) cohorts using the models from PredictDB. Next, the quadratic metabolic transformation algorithm (qMTA) is used to integrate the organ-specific transcript abundances and reference flux distribution and compute personalised organ-specific metabolic flux maps. The resulting flux maps can be used to perform FWAS to complex traits or diseases such as blood metabolic features or coronary artery disease. A hypothetic representation of an organ-specific solution space, reference flux distribution, and a set of three personalised flux distributions is shown for a reaction network with three fluxes (vx, vy and vz).