Fig. 1.
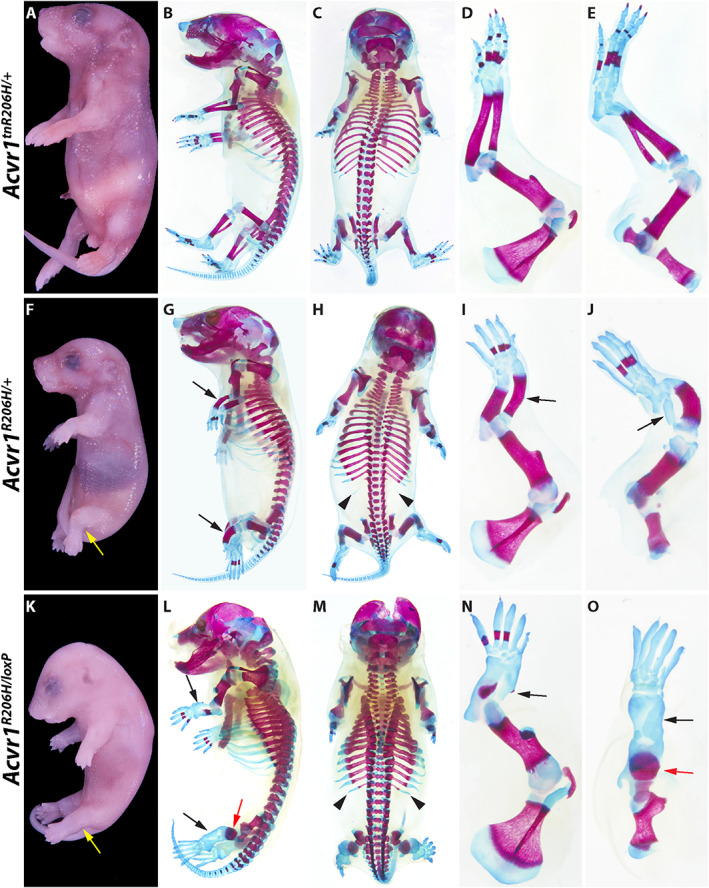
Representative examples of severe skeletal malformations caused by prenatal expression of Acvr1 R206H . (A–E) Acvr1 tnR206H/+ control P0 neonate. (F–J) Acvr1 R206H/+ neonate. (K–O) Acvr1 R206H/loxP neonate. Developmental defects are aggravated by loss of the wild‐type Acvr1 allele. (A, F, K) Whole‐mount views after skin removal. Yellow arrows indicate abnormal positioning of the hindlimbs. Left side (B, G, L) and dorsal (C, H, M) views of ABAR‐stained whole‐mount neonates. ABAR‐stained left forelimbs (D, I, N) and hindlimbs (E, J, O). Black and red arrows indicate severely shortened zeugopodal bones and femur, respectively; black arrowheads indicate L1 supernumerary ribs. Also note missing or abnormal ossification centers and thickened ribs in Acvr1 tnR206H/+ and Acvr1 R206H/loxP neonates. Additional defects are described in the text.
