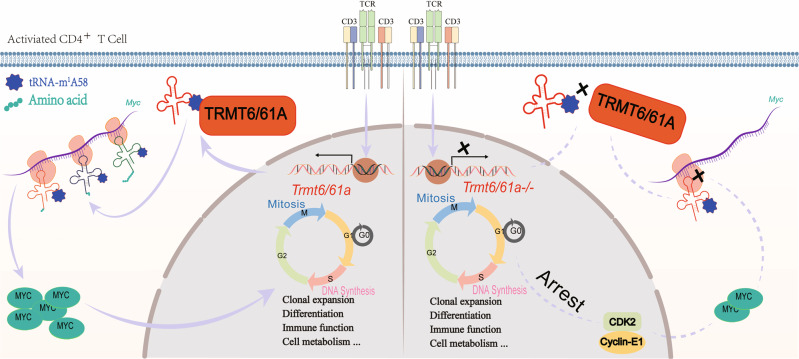
Fig. 1.
TRMT6/61A-mediated CD4+ T-cell activation through MYC synthesis. Upon CD4+ T-cell activation, Trmt61a is upregulated, leading to an increase tRNA-m1 A58 modification abundance, thus ensuring Myc translation, which is critical for mitosis and cell cycle progression. Myc also initiates the adaptive immune response, including clonal expansion, differentiation and effector functions. Specific deletion of Trmt61a in CD4+ T cells disrupted tRNA-m1 A58 modification and inhibited MYC translation, downregulating CDK2 and Cyclin-E1 and thus arresting the cell cycle.