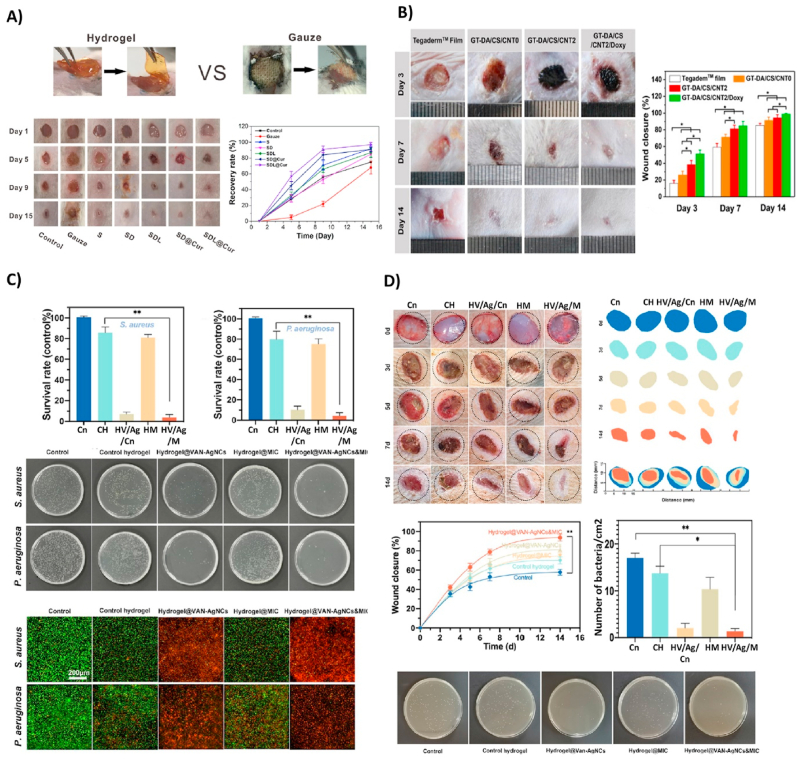
Fig. 6.
(A) Representative imaging of S. aureus-infected wound in a mouse model (15-day wound healing treated with the SDL@Cur hydrogel SDL, SD, S, and gauze). Reproduced with permission [198]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (B) Wound infection treated with TegadermTM film, GT-DA/CS/CNT0, GT DA/CS/CNT2, and GT-DA/CS/CNT2/Doxy hydrogel and the percentage of wound closure for each group. Reproduced with permission [195]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier. (C) Antimicrobial activity treated with hydrogel VAN-AgNCs and hydrogel MIC@NIM, hydrogel VAN-AgNCs-MIC@NIM, and control against S. aureus (A) and P. aeruginosa. (D) Infected diabetic wound healing treated with hydrogel VAN-AgNCs, hydrogel MIC@NIM, hydrogel VAN-AgNCs-MIC@NIM, and the control. Also, the wound closure and colony count results after seven days are presented. Reproduced with permission [217]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (Cn: Control, CH: Control Hydrogel, HV/Ag/Cn: hydrogel VAN-AgNCs, HM: hydrogel MIC@NIM, HV/Ag/M: hydrogel VAN-AgNCs-MIC@NIM).