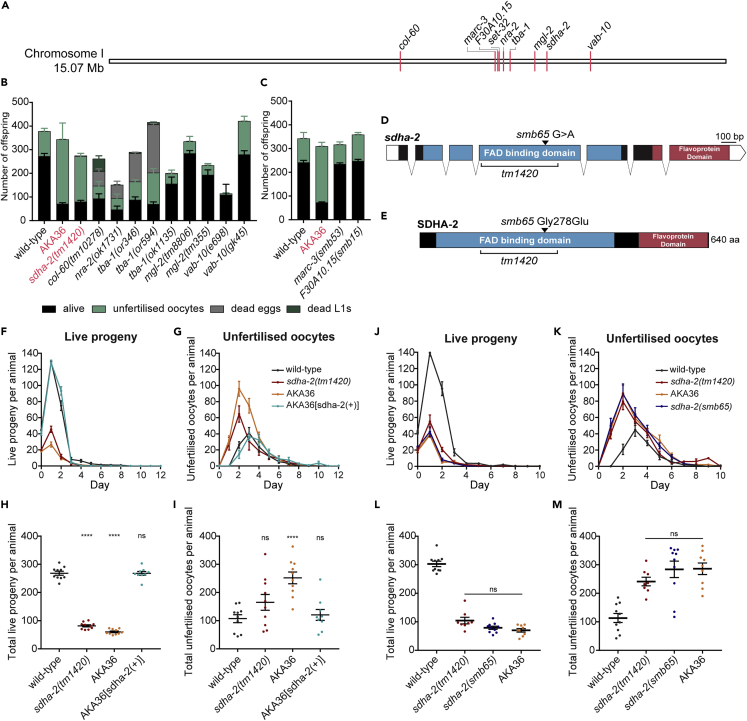
Figure 1.
sdha-2 mutant animals display a brood size defect
(A) Whole-genome sequencing of AKA36 revealed 9 non-synonymous mutations on Chromosome I, in addition to the previously characterized set-32(ok1457) deletion.
(B and C) Brood size screen of the candidate genes identified by AKA36 whole genome sequencing. (B) Publicly available strains. (C) Strains created by CRISPR-Cas9, recreating the mutations from AKA36 in the wild-type background. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 5-10.
(D) Schematic representing the sdha-2 transcript. Exons are represented by black boxes, introns by connecting lines, and untranslated regions by white boxes. bp denotes length in base pairs.
(E) Predicted SDHA-2 protein. aa denotes length in amino acids.
(D and E) The sequence encoding the FAD binding domain is indicated in blue and the succinate dehydrogenase/fumarate reductase flavoprotein C-terminal domain (flavoprotein domain) is in maroon. AKA36 carries a Gly > Glu substitution in SDHA-2 at position 278 (arrow). sdha-2(tm1420) has a 173 aa in-frame deletion (bracket).
(F–I) Brood size assay characterizing sdha-2 mutant infertility. (F and G) The average number of (F) live progeny and (G) unfertilized oocytes produced per animal per day. (H and I) The total number of (H) live progeny and (I) unfertilized oocytes per animal. AKA36[sdha-2(+)] was generated by repairing the sdha-2 SNV in AKA36 back to the wild-type sequence by CRISPR-Cas9. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 9-10. Comparisons are between the indicated strain and wild-type and were performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001.
(J–M) Brood size assay comparing different sdha-2 mutations. (J and K) The average number of (J) live progeny and (K) unfertilized oocytes produced per animal per day. (L and M) The total number of (L) live progeny and (M) unfertilized oocytes per animal. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 9-10. Comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.