Figure 4.
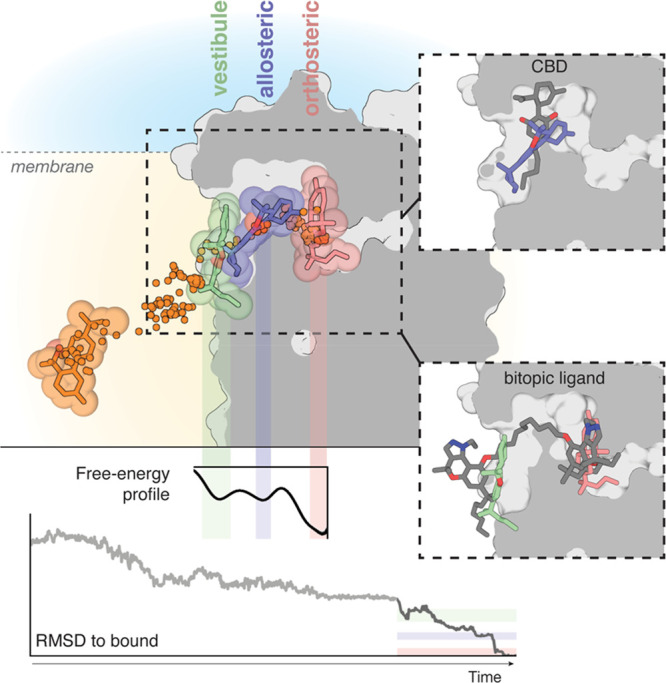
The binding pathway of JWH-133 to the orthosteric site of CB2R. JWH-133 (in orange) diffuses through the membrane to reach a minimum in the free-energy profile in which JWH-133 (in green) contacts a membrane vestibule or lipid-facing cavity. Subsequently, JWH-133 (in blue) moves to a second allosteric minimum or bundle-facing cavity in the trajectory. Finally, JWH-133 (in pink) moves to the most stable minimum in the pathway at the orthosteric binding site. Ligand positions during the pathway are shown by dots. RMSD values (light gray from unbiased MD simulations, dark gray from well-tempered metadynamics) relative to the reference docked binding mode of JWH-133 at the orthosteric site and a representative free-energy profile obtained in well-tempered metadynamics are shown. Color bars indicate the different locations of the ligand. Comparison of our previously reported binding mode of the negative allosteric modulator cannabidiol (CBD, gray)63 and JWH-133 at the allosteric minimum or bundle-facing cavity (in blue), and the binding mode of a bitopic ligand (compound 22, gray)78 and JWH-133 at the vestibule or lipid-facing cavity (in green) and the orthosteric binding site (in pink).
