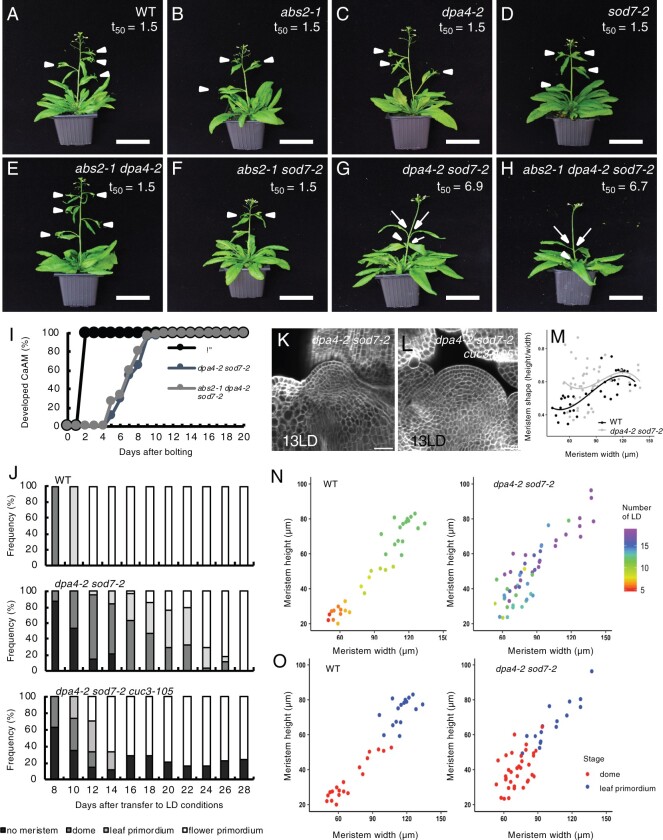
Figure 2.
DPA4 and SOD7 are required for the rapid development of CaAMs. A–H, Inflorescences of WT, single, double, and triple ngal mutants. Plants were grown for 5 weeks in LD conditions. White arrowheads point to developed CaAMs, while the arrows point to delayed CaAMs. The time point after bolting at which half of the CaAMs are developed (t50, in days) is indicated under the genotype. I, Kinetics of CaAM development after bolting. Development of the CaAM is indicated as the percentage of developed branches (≥3 mm) to the total number of cauline leaves (n ≥ 11). J, Kinetics of CaAM development in WT, dpa4-2 sod7-2, and dpa4-2 sod7-2 cuc3-105 grown for 4 weeks in SD and transferred to LD (n ≥ 10). K and L, Tangential optical sections of calcofluor-stained WT of dpa4-2 sod7-2 (K) and dpa4-2 sod7-2 cuc3-105 (L) CaAM at 13LD. The WT control is shown in Figure 1D. M, Evolution of CaAM shape in WT and dpa4-2 sod7-2. N, CaAM height and width as a function of the number of days grown under LD conditions (number of LD; shown on the right) in WT and dpa4-2 sod7-2. O, CaAM height and width as a function of the CaAM stage (dome or leaf primordium) in WT and dpa4-2 sod7-2. Scale bars: (A–H) = 5 cm; (K and L) = 100 µm.