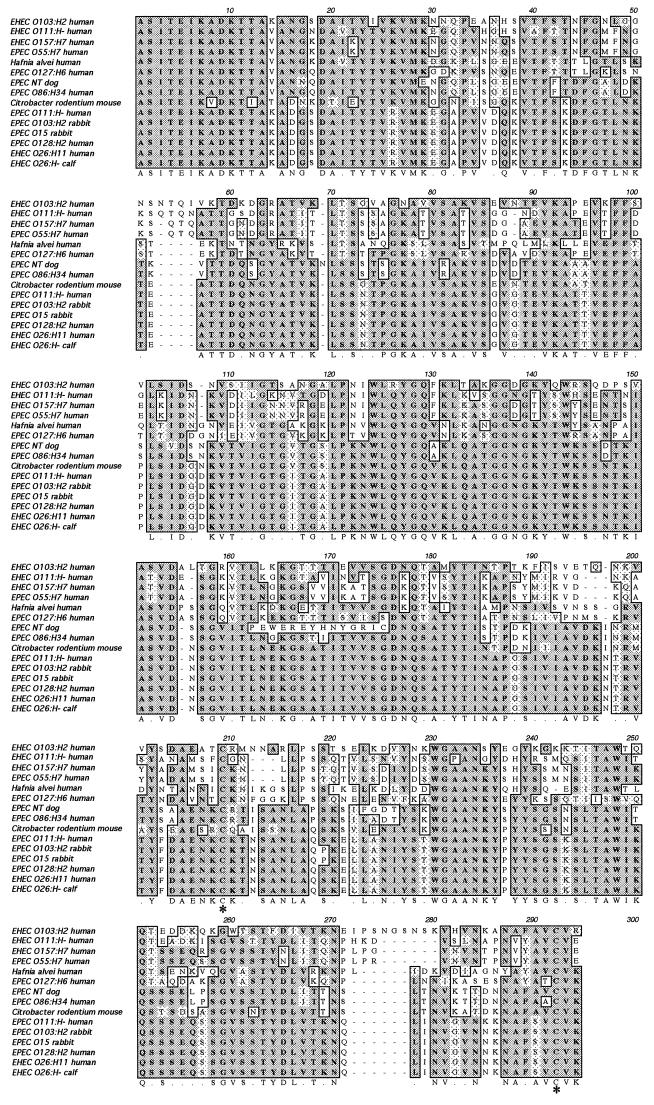
FIG. 1.
CLUSTAL W alignment of intimin ɛ sequence (AF116899) from the EHEC O103:H2 strain PMK5 with α, β, γ and δ intimins cloned from different pathogenic E. coli (EPEC or EHEC), an intimin homologue from H. alvei, and an intimin homologue from C. rodentium. The accession numbers in GenBank for these sequences and the names of the bacterial strains are given in Materials and Methods. Of note, a recent study (35) suggests that the H. alvei strains containing the intimin gene are, in fact, unusual biotypes of E. coli or represent a new species in the genus Escherichia. The multiple alignment was based on the last C-terminal amino acids of the different intimin (starting with alanine 658). The two cysteine residues necessary for the formation of a disulfide bond and the binding activity are indicated by asterisks.