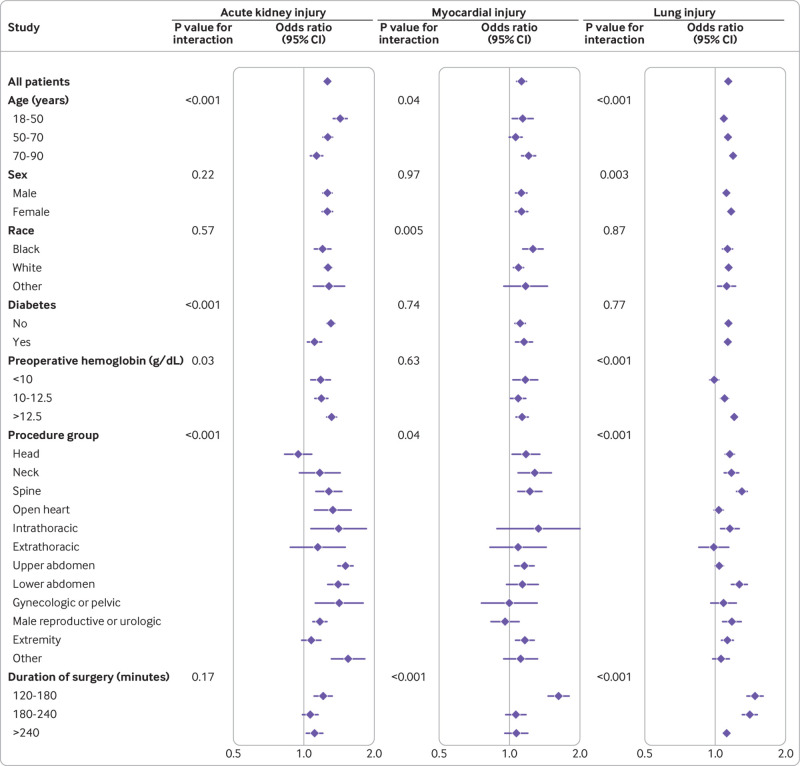
Fig 3.
Associations between increased intraoperative oxygen exposure and acute kidney injury, myocardial injury, and lung injury in all patients and in subgroups, adjusted for impact of factors included as covariates (age, sex, race, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists status, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Elixhauser comorbidity index, chronic pulmonary disease, emergency surgery, preoperative serum creatinine, hemoglobin, troponin and lactate concentrations, nitrous oxide exposure, median tidal volume, median intraoperative positive end expiratory pressure, volumes of intraoperative intravenous crystalloid and packed red blood cells administrations, and intraoperative hypotension). Point estimates and bars represent odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for organ injury associated with 75th centile compared with 25th centile of AUCFIO2. P values represent statistical significance for each factor to modify association between oxygen exposure and organ injury, assessed with multiple degree of freedom test. AUCFIO2=area under the curve of FIO2 (fraction of inspired oxygen) above 21% during minutes when the corresponding oxygen saturation was >92%