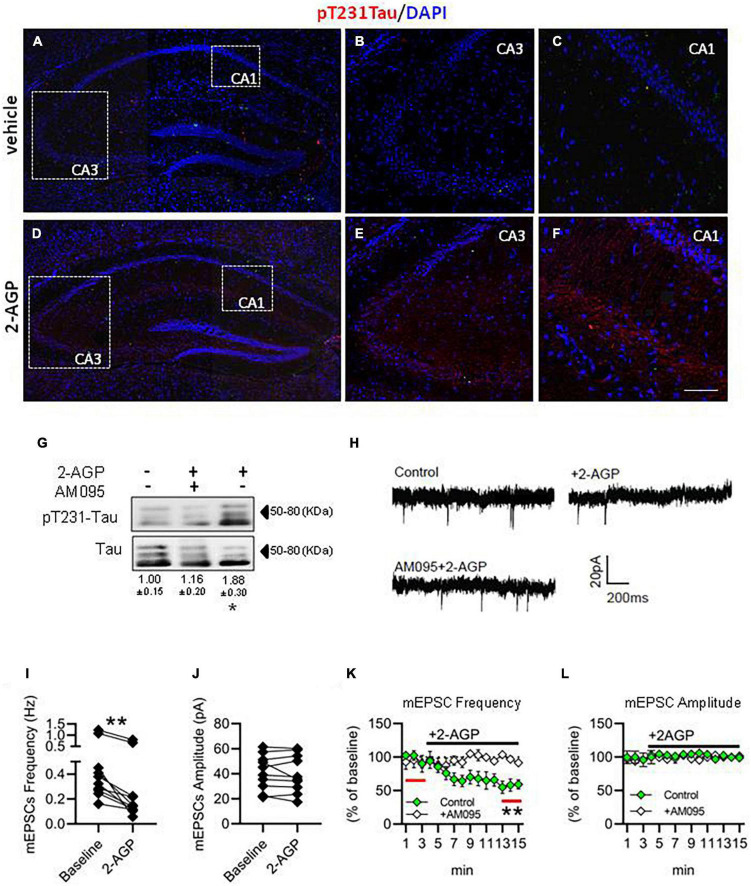
FIGURE 4.
2-AGP triggers pT231-Tau phosphorylation and impairs glutamatergic transmission in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. (A–F) Representative images of pT231-Tau immunoreactivity in the hippocampus showing the highest expression in the CA3-CA1 area of 2-AGP-injected mice. Panels (B,C,E,F) are high magnification of the respective area selected by the dotted box in the panels (A,D). Scale bar: 150 μm in (A,D) and 100 μm in (B,C,E,F). (G) Representative immunoblots of pT231-Tau/Tau ratios showing the effect of 2-AGP (10 mg/kg, 1 h) or AM095 treatment (10 mg/kg), injected, 1 h before 2-AGP. Optical density (OD) values are expressed as the ratio between the OD values of phosphorylated and total protein. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 3 mice/group), *p < 0.05, statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test. (H) Representative recordings traces of mEPSCs in CA1 pyramidal neurons in control, 2AGP and AM095 + 2-AGP. (I) Graph of the mEPSC frequency before (3 min) (0.48 ± 0.11 Hz) and after treatment with 250 nM 2-AGP (3 min) (0.25 ± 0.08 Hz), Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. **p < 0.01, n = 10 neurons in 4 mice (J) Graph of the mEPSC amplitude before (41.28 ± 4.4 pA) and after 2-AGP (40.10 ± 4.7 pA), n = 10 neurons in 4 mice. (K) mEPSC frequency (% of 3 min of baseline). Green: effect of the 2-AGP treatment in CA1 pyramidal neurons, white: effect of the 2-AGP treatment in pyramidal neurons pre-treated with AM095 (10μM), statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed one sample t-test, **p < 0.05; red lines represent the part of compared graph. (L) mEPSC amplitude (% of the baseline). Green: effect of the 2-AGP treatment in CA1 pyramidal neurons, white: effect of the 2-AGP treatment in pyramidal neurons pre-treated with AM095.