Figure 1.
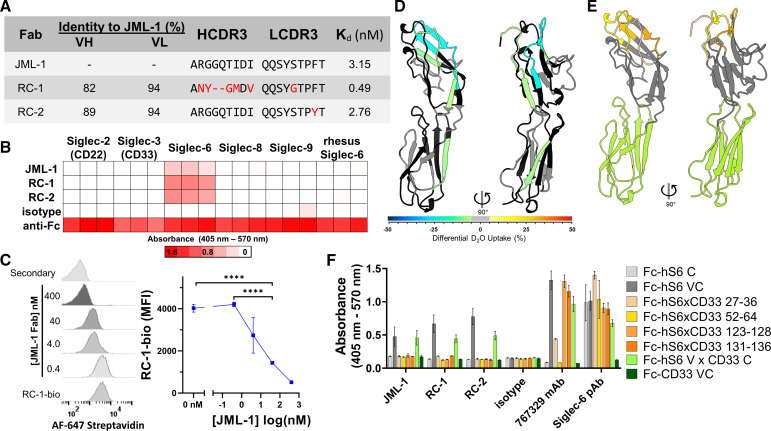
Siglec-6-targeting antibody clones selected from a post-alloHSCT library exhibit specificity and shared epitope. (A) Comparison of post-alloHSCT antibody clones including VH and VL amino acid sequence identities, IMGT-defined CDR3 alignments, and affinity data from SPR analysis of Fab binding to Siglec-6–Fc fusion protein. (B) Heatmap of ELISA data (triplicate) from directly coating human or rhesus (85% amino acid sequence identity within the ectodomain) Siglec–Fc fusion proteins, incubating with Fabs, and detecting with antihuman Fab or antihuman Fc (positive control). The post-alloHSCT Fabs are all specific for human Siglec-6. (C) Flow cytometry histograms (left) and quantification (right) demonstrating that JML-1 Fab can block the binding of biotinylated RC-1 (RC-1-bio) Fab (40 nM) by competing for Siglec-6 on the surface of U937 cells. Statistics (n=3) were calculated using Student’s t-test. ****p<0.0001. (D) Homology model of Siglec-6 (V and C2i domains, 27–236; see online supplemental material), colored according to the differential deuterium uptake in the presence of RC-1 Fab as determined by HDX-MS. Negative differential D2O values represent decreased solvent exposure in the presence of Fab. Black regions were not observed, and gray regions indicate no significant change in deuterium uptake. (E) Homology model of Siglec-6 illustrating with shades of yellow and orange the peptides that were individually substituted with corresponding CD33 sequences, and green indicating the C2i domain that was replaced entirely for epitope mapping. (F) Epitope mapping ELISA with Siglec-6×CD33 chimeric Fc-fusion proteins indicating the dependence of the mutated regions for binding with human Fabs but not for the commercial mouse mAb or sheep pAb to human Siglec-6 (hS6). alloHSCT, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; C2i, C2-type I; CDR3, complementarity determining region 3; HDX-MS, hydrogen–deuterium exchange mass spectrometry; mAb, monoclonal antibody; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; pAb, polyclonal antibody; SPR, surface plasmon resonance; VH, variable heavy; VL, light chain domain.