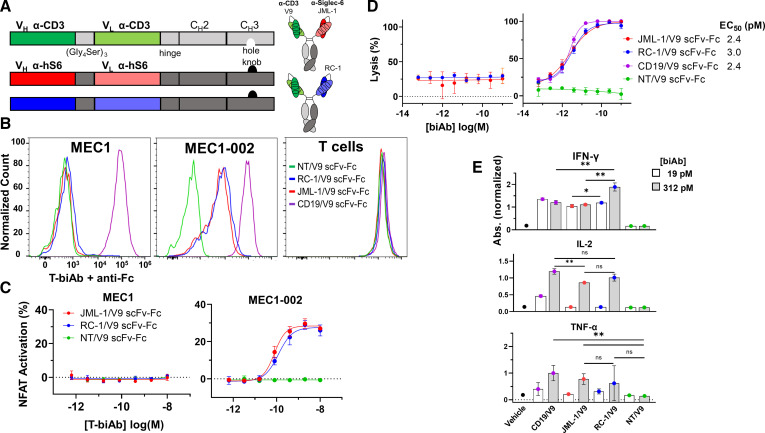
Figure 2.
scFv–Fc T-biAbs mediate specific T-cell activation and CLL lysis. (A) T-biAbs were designed with scFv domains fused to human IgG1 Fc with knob-into-hole mutations to facilitate heterodimerization of Siglec-6 and CD3 binding arms. (B) Siglec-6− CLL cell line MEC1 (left), Siglec-6+ MEC1-002 (middle), and human T cells (right) were stained with 10 µg/mL of scFv–Fc T-biAb and an antihuman Fc secondary antibody to validate bispecificity for Siglec-6 (or CD19 as positive control) and CD3. (C) A Jurkat-Lucia NFAT reporter cell line was cultured overnight with scFv–Fc T-biAbs and MEC1 (left) or MEC1-002 (right) cells to determine T-cell activation in the absence or presence of target expression. (D) MEC1 (left) and MEC1-Siglec-6 (hS6) transgenic (right) cell lines were cocultured with human T cells and a titration of the indicated T biAbs. Following overnight incubation, cell lysis was assessed by intracellular luciferase activity. (E) The levels of type I cytokines in the cell lysis assay supernatants were determined by ELISA, and data were normalized to the CD19/V9 positive control. Statistics were calculated using an unpaired t-test, n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IL, interleukin; ns, not significant; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; T-biAb, T cell-recruiting bispecific antibody; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; VH, variable heavy chain domain; VL, variable light chain domain.