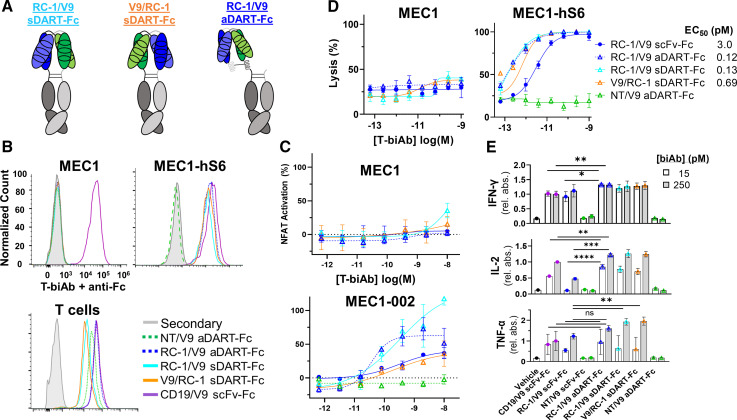
Figure 3.
DART–Fc T-biAbs elicit more potent activation and lysis than scFv–Fc. (A) Cartoon depiction of Siglec-6×CD3 DART–Fc constructs. In all three constructs, Fc dimerization was mediated by knob-into-hole mutations. Two sDART constructs were made, alternating the positioning of VL and VH for each clone. sDART–Fc T-biAbs are labeled in terms of the VL clone at the N-terminus of the hole–Fc chain, RC-1/V9 sDART–Fc and V9/RC-1 sDART–Fc. The aDART–Fc construct consists of three polypeptide chains and was made by inserting oppositely charged coiled-coil domains at the C-terminus of each VH domain to stabilize the interaction between the free VL–VH chain and the two chains with dimerized Fc domains. (B) Siglec-6− CLL cell line MEC1, Siglec-6+ MEC1-hS6, and human T cells were stained with 10 nM of DART–Fc T-biAb and an antihuman Fc secondary antibody to validate T-biAb specificity for Siglec-6 (or CD19 as positive control) and CD3. (C) A Jurkat-Lucia NFAT reporter cell line was cultured overnight with scFv–Fc T-biAbs and MEC1 or MEC1-002 CLL cell lines (E:T=1:1) to determine T-cell activation in the absence or presence of target expression. (D) MEC1 and MEC1-hS6 cell lines were cocultured with human T cells (E:T=1:1) and a titration of the indicated T-biAbs. Following overnight incubation, cell lysis was assessed by intracellular luciferase activity. (E) Cytokine levels in the culture media from the overnight cytotoxicity assay were determined by ELISA, and data were normalized to the CD19/V9 positive control at the high dose (250 pM). Statistics were calculated using an unpaired t-test, n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. aDART, asymmetrical dual-affinity retargeting; DART, dual-affinity retargeting; E:T, effector-to-target; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IL, interleukin; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; ns, not significant; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; sDART, symmetrical dual-affinity retargeting; T-biAb, T cell-recruiting bispecific antibody; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.