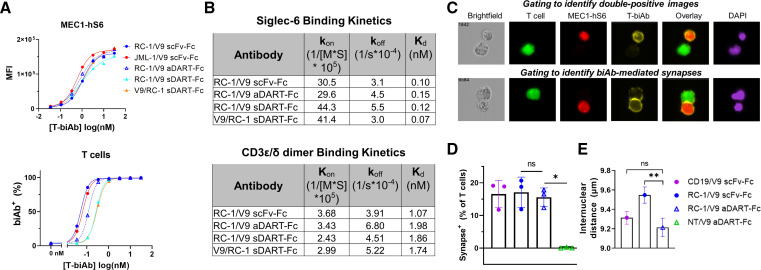
Figure 5.
aDART–Fc binds with similar affinity but creates a shorter synapse than scFv–Fc. (A) MEC1-hS6 (top) or primary human T cells (bottom) were stained with a titration of T-biAbs, and binding was detected by the addition of an antihuman Fc secondary antibody. (B) RC-1/V9 T-biAbs were immobilized to a CM5 Biacore chip via the Fc domain, soluble Siglec-6 or CD3ε/δ dimer was injected, and SPR sensorgrams were used to determine kon, koff, and Kd. (C) FarRed-labeled MEC1-hS6 cells (1×106 cells) were bound with 50 nM T-biAb, washed, and cocultured with CFSE-labeled Jurkat cells (1×105 cells) for 1 hour at 37°C followed by fixation, permeabilization, and staining with Cy3-conjugated antihuman Fc and DAPI. Samples were processed on an Amnis ImageStreamx MK II (Luminex) instrument and analyzed by IDEAS V.6.3 software to identify CFSE+/FarRed+ images (top) and T-biAb+ synapses (bottom). (D) The percentage of T cells forming synapses was quantified for three independent experiments and data were compared using a paired t-test. (E) Internuclear distance was calculated by measuring the distance between synapse-positive cells in the DAPI channel. The mean and SE of the mean for approximately 1000 events per sample are plotted from one representative experiment and statistics were calculated using an unpaired t-test, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. aDART, asymmetrical dual-affinity retargeting; CFSE, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; SPR, surface plasmon resonance; T-biAb, T cell-recruiting bispecific antibody.