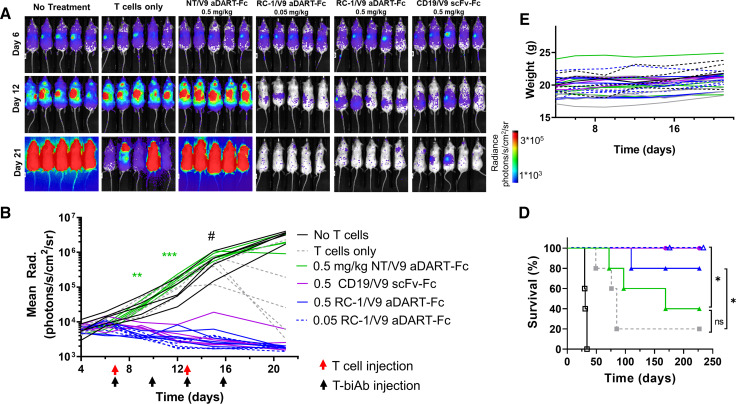
Figure 6.
RC-1/V9 aDART–Fc clears CLL cells in a CDX model. NSG mice were inoculated intravenously with 2×106 MEC1-fLuc-hS6 cells and on day 7 were treated with 3×106 T cells intravenously, followed by treatment two times per week with T-biAb (0.5 mg/kg or 0.05 mg/kg) for 2 weeks. On day 13, mice received a second injection of only 1×106 T cells. (A) Bioluminescence images and (B) quantification (one line per mouse) showed complete clearance of CLL cells in mice treated with T cells and CD19/V9 or RC-1/V9 T-biAbs, but not the NT/V9 T-biAb. Statistics were calculated comparing both doses of RC-1/V9 with NT/V9 using an unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction, n=5 mice per group (**p<0.01, ***p<0.001, # = image saturation). (C) Weight loss was not observed in any animals over the course of treatment. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that RC-1/V9 (0.05 mg/kg) and CD19/V9 (0.5 mg/kg) both improved survival over the NT/V9 control (0.5 mg/kg). Statistics were calculated using the Mantel-Cox log-rank analysis, HR=9.95 (*p<0.05). aDART, asymmetrical dual-affinity retargeting; ns, not significant; NT, non-targeting; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; T-biAb, T cell-recruiting bispecific antibody.