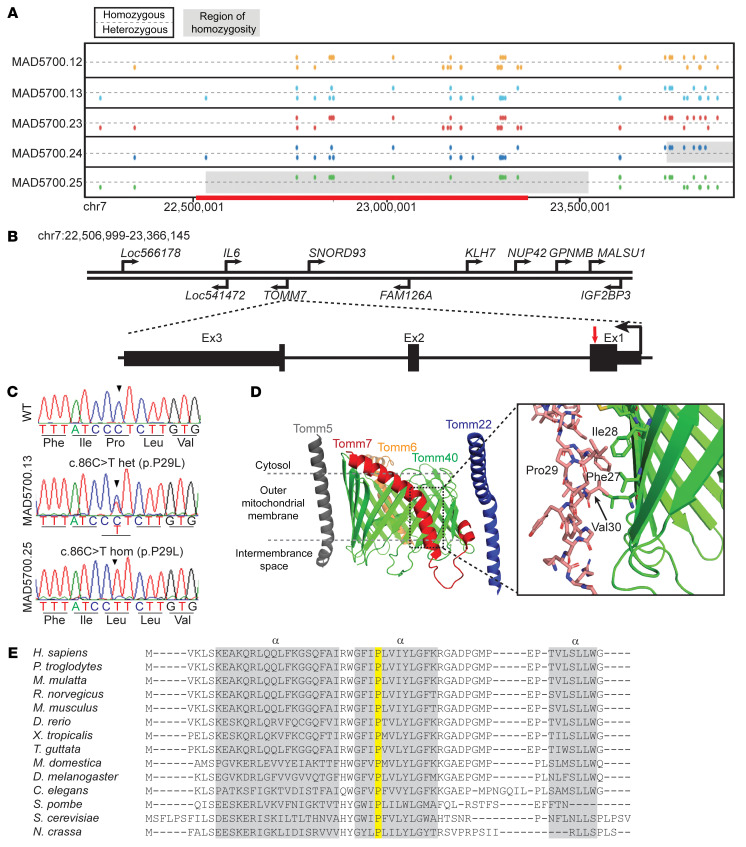
Figure 2. Identification of a Pro29Leu variant in the TOMM7 gene.
(A) Schematic of segments on chromosome 7 of the proband (MAD5700.25) and his parents (MAD5700.12, 13) and sisters (MAD5700.23, 24), based on GRCh37/hg19 coordinates. For each individual, the top line displays markers with homozygous genotypes and the bottom line displays markers with heterozygous genotypes. The homozygous regions inferred from WES data are shown in gray (~1 Mb) and those derived from WGS (~0.8 Mb, chr7:22,506,999-23,366,145) shown with red. The two siblings of the proband and the parents did not share the homozygous region. (B) The location of various genes in the homozygous region on chromosome 7, the gene structure of TOMM7, and the location of the mutation in the proband. Human TOMM7 contains three exons (shown in black rectangles) and two introns (shown as a line). The pathogenic variant c.86C>T in TOMM7 is located in exon 1 (red arrow). (C) Sequence electropherogram for WT (top) sequence in exon 1 of TOMM7, MAD5700.12 (middle) showing heterozygous (het) c.86C>T variant, and MAD5700.25 (bottom) showing the homozygous (hom) c.86C>T variant. (D) An overview of the cryo-electron microscope structure for human TOM complex (PDB ID 7CK6). TOMM7 is shown in red, TOMM5 in gray, TOMM6 in orange, TOMM22 in blue, and TOMM40 in green. The expanded view shows the region surrounding residue proline (Pro) 29 in TOMM7, with nearby amino acids phenylalanine (Phe) 27, isoleucine (Ile) 28, and valine (Val) 31 forming interactions with TOMM40 (green). (E) Protein alignment of TOMM7 from the indicated organisms. Note that Proline 29 (highlighted in yellow) is conserved amongst all the phyla aligned. The three α-helices are indicated by gray bars.