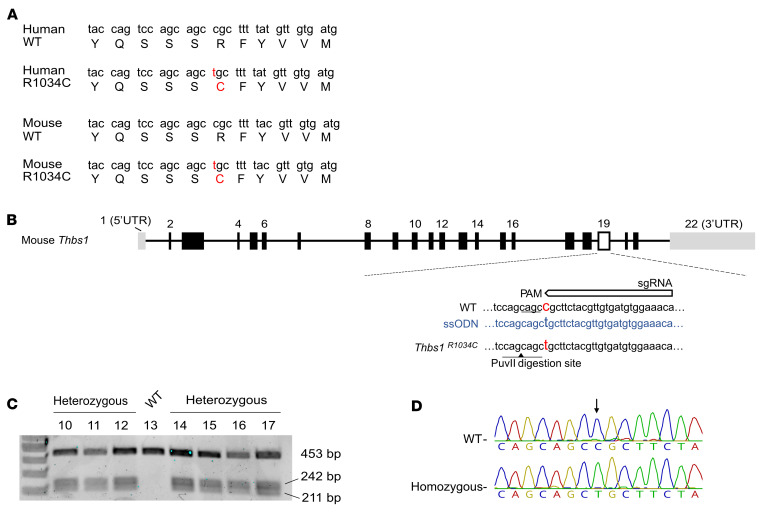
Figure 2. Generation of Thbs1R1034C mice.
(A) CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing was used to generate the R1034C mutation in murine Thbs1. The R1034 sequence codon is conserved between humans and mice. (B) Strategy for single-stranded oligo DNA nucleotide–mediated (ssODN-mediated) knockin with CRISPR/Cas9. Successful mutagenesis generated a PuvII digestion site (black arrowhead) (C). Mutants were confirmed by the presence of 242 and 211 bp bands following PCR and PuvII digestion. (D) Sanger sequencing confirmed the F1 homozygous versus littermate WT from heterozygous founders in C. RNA purified from F1 homozygous mutants also confirmed the point mutation (Supplemental Figure 2).