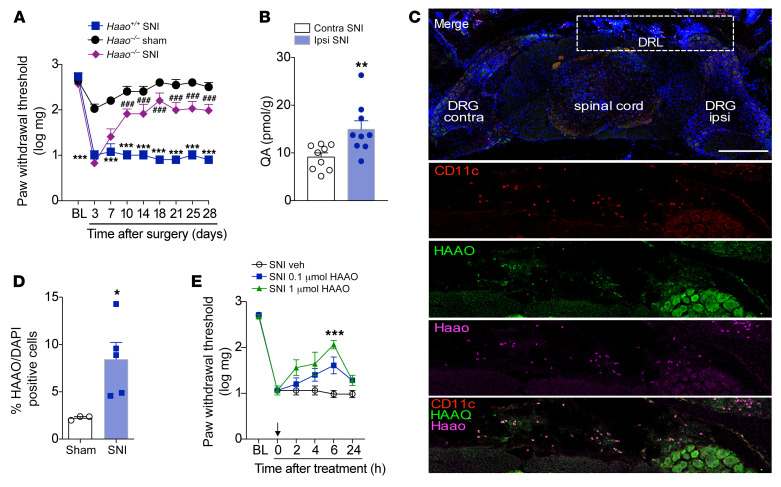
Figure 10. HAAO-derived QA mediates neuropathic pain through the upmodulation of NMDA currents.
(A) Mechanical nociceptive threshold was evaluated before and up to 28 days after SNI and sham surgeries in 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid dioxygenase–knockout (Haao–/–) and Haao+/+ mice (n = 4–8). (B) Levels of quinolinic acid (QA) were determined in the contralateral and ipsilateral dorsal horn of the spinal cord of mice after SNI surgery (14 days after surgery; n = 9). (C) Representative images of in situ hybridization (RNAscope) analysis of Haao (magenta) triple stained for HAAO (green) and CD11c (red) immunoreactivity and DAPI (cell nuclei, blue) in the ipsilateral region containing DRG (L4), DRL, and spinal cord from mice harvested 14 days after SNI surgery. Scale bar: 128 μm. (D) Quantification of Haao and HAAO-expressing cells in the DRL from SNI mice (14 days after SNI) or sham mice (n = 3–5). (E) Mechanical nociceptive threshold was determined before and 14 days after SNI. Mice were treated intrathecally with vehicle or HAAO inhibitor (0.1 and 1 μmol) and mechanical allodynia was measured up to 24 hours after treatment (n = 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus sham or vehicle; ###P < 0.001 versus Haao–/– mice by 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (A and E) or unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test (B and D).