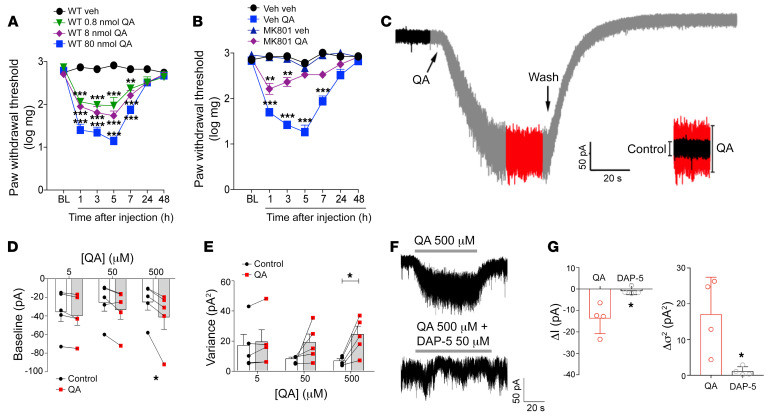
Figure 11. The pronociceptive activity of QA depends on upmodulation of NMDA currents.
(A) Mechanical nociceptive thresholds were evaluated before and up to 48 hours after intrathecal (i.t.) injection of quinolinic acid (QA; 0.8–80 nmol) or vehicle (saline) in WT mice (n = 5). (B) Mechanical nociceptive threshold was evaluated before and up to 48 hours after i.t. injection of QA (80 nmol) in mice pretreated with MK801 (10 nmol) or vehicle (n = 4–5). (C) Representative trace and (D) quantification of QA (5–500 μM) eliciting an inward current (n = 5) and promoting an augmentation in peak-to-peak noise variance (E, n = 5) in spinal cord neurons. (F and G) Both effects were antagonized by the NMDA antagonist DAP-5 (50 μM, n = 4). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle, treatment, or current baseline by 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (A and B), paired 2-tailed Student’s t test (D and E), or unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test (G).