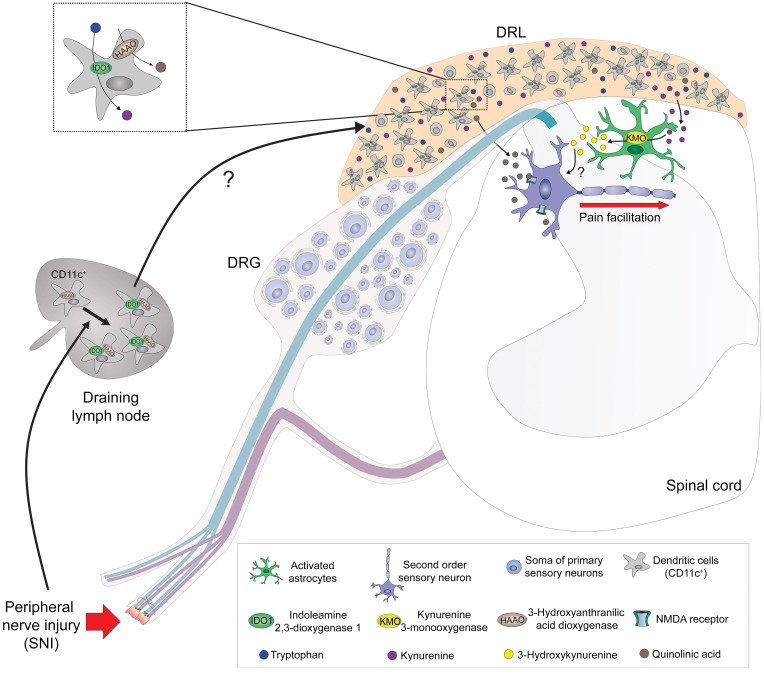
Figure 12. Schematic representation of the role of the kynurenine pathway in the maintenance of neuropathic pain.
After peripheral nerve injury, there is an up regulation of IDO1 in dendritic cells (DCs), which accumulate in the dorsal root leptomeninges (DRLs), leading to an increase in the levels of kynurenine (Kyn) in the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, Kyn is metabolized by astrocyte-expressed KMO into a potent pronociceptive metabolite, 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-Hk). Additionally, HAAO-expressing DCs in (DRLs) might be responsible for the increase in the levels of QA in the spinal cord. QA is also a pronociceptive molecule in the spinal cord, acting through an enhancement of glutamatergic NMDA transmission and consequently to maintain pain hypersensitivity.