Figure 4. miR-956 regulates the Notch signaling pathway via insv.
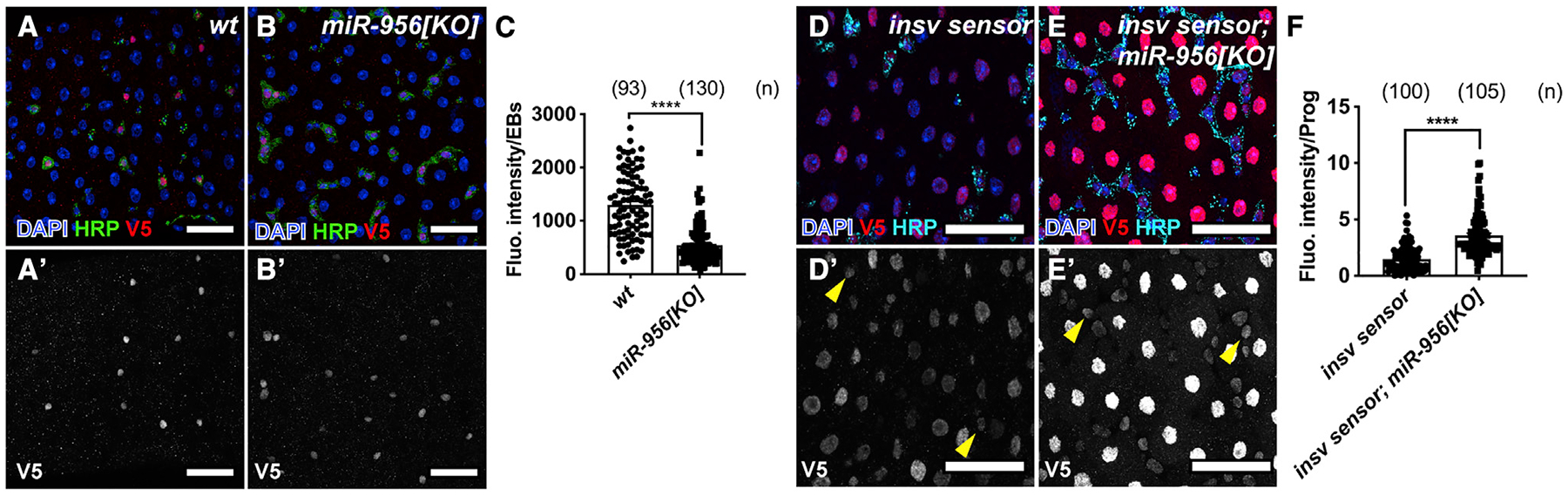
(A and B) Notch signaling reporter expression (anti-V5 in red) in (A) wild type and (B) miR-956[KO] mutants counterstained for progenitors in HRP (green) and all cell nuclei (DAPI in blue). (A′–B′) Grayscale images of Notch signaling reporter in wild type versus miR-956[KO] mutants.
(C) Fluorescence intensity of Notch reporter expression in EBs in wild type versus miR-956[KO] mutants.
(D and E) Midguts from (D) control or (E) miR-956[KO] mutants stained for smGFP.V5.insv 3′UTR (red), progenitors in HRP (cyan), and all cell nuclei (DAPI in blue).
(D′–E′) Grayscale images of indicated channels from (D) and (E). Progenitor cells are labeled with yellow arrowheads.
(F) Fluorescence intensity of V5 reporter expression in progenitors of control and miR-956[KO] mutants stained for smGFP.V5.insv 3′UTR (red).
Data shown as mean ± SEM. Significance values: ****p < 0.0001. Scale bar, 25 mm. n values in the graphs indicate the number of cells quantified from at least five intestines.
