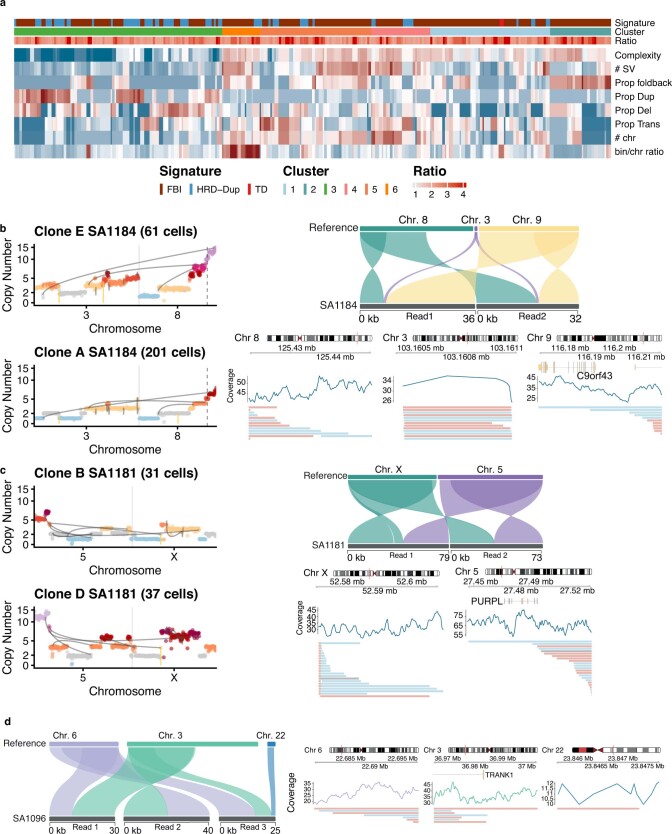
Extended Data Fig. 9. Genomic features of HLAMPS and long read sequencing validation.
a) Each column is a HLAMP that amplifies an oncogene. Each row is a feature extracted from a region 15Mb either side of the amplification. Complexity = entropy of haplotype-specific states, #SV = total number of structural variants identified, proportion of SVs of each type: fold-back inversions, duplications, deletions and translocations. #chr = number of chromosomes involved in translocation. bin/chr ratio copy number of the bin containing the oncogene to the average copy number across the chromosome. Ratio is the copy number ratio between the clone with the maximum copy number state and the minimum copy number state. b–c) HLAMPs involving multiple chromosomes, left plot shows copy number profiles from pseudobulk clones derived from DLP, lines indicate rearrangement breakpoints, right plot shows example long reads from Oxford nanopore technologies that support inter-chromosomal translocations. Example reads and their mapping to chromosomes of interest (top right), long-read coverage of genomic region and alignment of all supporting reads (bottom right). b) SA1184 MYC amplification c) SA1181 chr5q amplification. d) Long-read support for inter-chromosomal alterations involving chromosomes 3 and 6 in SA1096, DLP clone-level plots shown in Fig. 4j.