Figure 3.
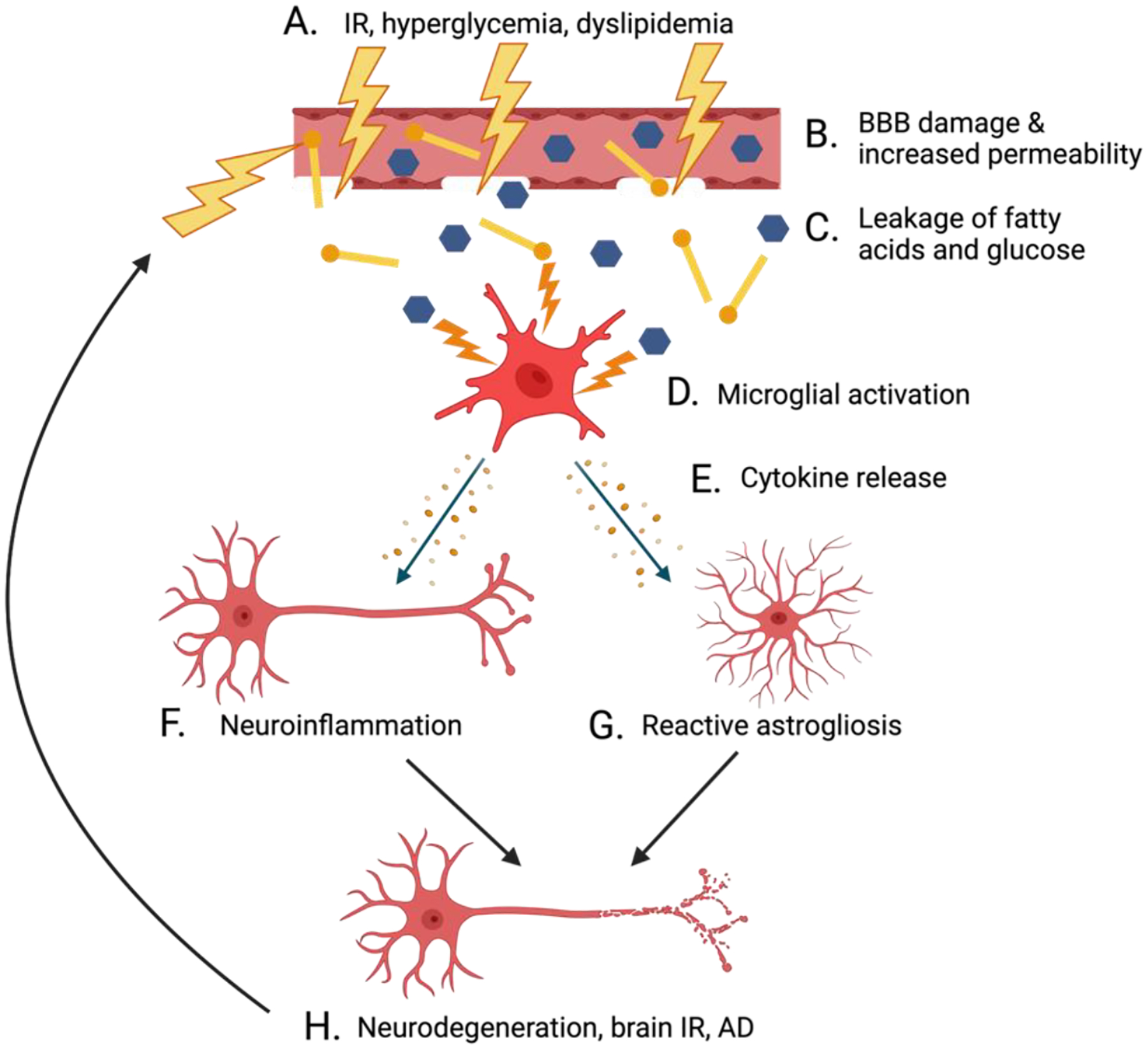
Interactions between IR, neuroinflammation, and neurodegenerative disease. Elevated blood sugar levels and dyslipidemia in the blood are consequences of IR (A) that can damage and increase permeability of the BBB (B). BBB damage results in the infiltration of the brain with free fatty acids and excessive glucose (C), thus activating microglia into a pro-inflammatory state (D). These activated microglia release cytokines (E) that stimulate neuroinflammation (F) and reactive astrogliosis (G). Chronic neuroinflammation fuels the development of brain IR, neurodegeneration, and the progression of AD (H).
