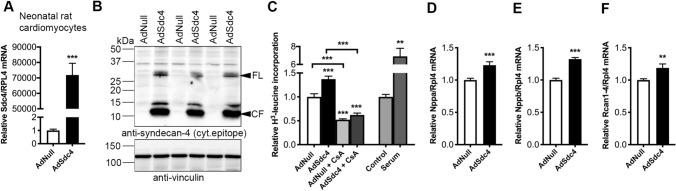
Fig. 5.
Cultured neonatal cardiomyocytes overexpressing Sdc4 show increased calcineurin-dependent hypertrophic growth and NFAT activation. A Relative mRNA level of Sdc4 in neonatal cardiomyocytes (NCM) from rats transduced with an adenovirus encoding Sdc4 (AdSdc4) or control (AdNull), n = 11–12. B Representative immunoblot (n = 3) showing increased full-length (FL) syndecan-4 protein and shedding, i.e., increased levels of the cellular fragment (CF) remaining in cells after shedding of the ectodomain, in NCM protein lysates. Vinculin was used for loading control. C Radioactive H3-leucine incorporation, used to estimate protein synthesis and hypertrophic growth in vitro, in NCM transduced with AdSDC4 or AdNull (n = 8), or co-treated with Cyclosporine A (CsA, n = 5–6), an inhibitor of calcineurin. Serum-treated cells served as positive control of growth (n = 3). Relative expression of signature molecules of heart failure, Nppa and Nppb [D, E; encoding atrial and brain natriuretic peptides (ANP and BNP, respectively)], and the nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT)-responsive gene Rcan1-4 (F) in NCM transduced with AdSdc4 or AdNull, n = 11–12. Data are mean ± SEM. Gene expression was normalized to Rpl4 (A and C–E). Statistical differences were tested using one-way ANOVA with Tukey´s multiple comparison test (C), or an unpaired t-test vs. AdNull (A and D–F), **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001