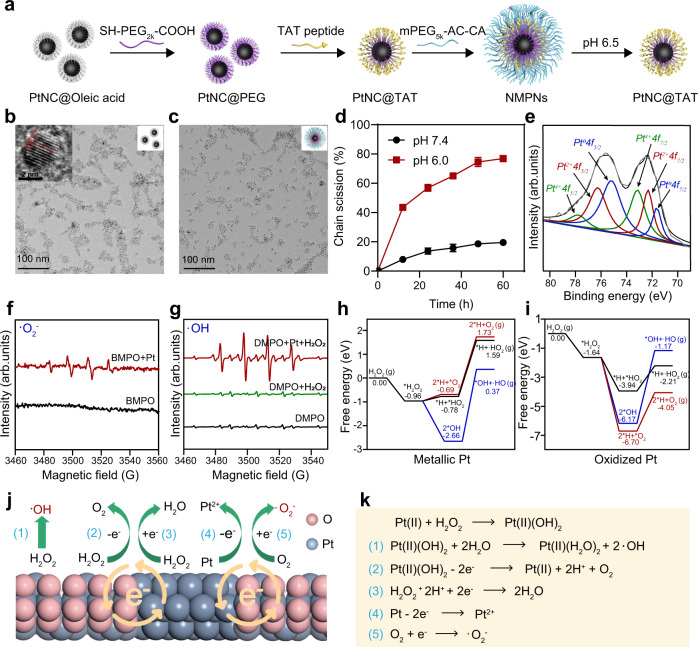
Fig. 2. Designed synthesis and characterization of NMPNs with high performance catalytic activity.
a Schematic diagram of the synthesis of NMPNs. b Representative TEM image of PtNCs in chloroform. Scale bar: 100 nm; Insert: high-resolution TEM image of PtNCs. Scale bar: 2 nm. n = 3 independent experiments. c TEM image of NMPNs in water. Scale bar: 100 nm. n = 3 independent experiments. d The analysis of shedding behaviour of mPEG5K-AC-CA from the surface of NMPNs at pH 6.5 and 7.4. Rhodamine B isothiocyanate (RITC) was conjugated to the terminal of mPEG5K-AC-CA to obtain RITC-mPEG5K-AC-CA, and the fluorescence intensity of RITC-mPEG5K-AC-CA fragments released from NTNPs surface was analyzed. n = 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t-test. e XPS spectra of NMPNs, confirming the co-existence of Pt0 (B.E. at 71.7 and 75.3 eV), Pt2+ (B.E. at 72.3 and 76.3 eV), and Pt4+ (B.E. at 73.1 and 77.9 eV) on the surface of NMPNs. f ESR spectra of NMPNs by using BMPO as spin-trapping agents for detecting •O2−. g ESR spectra of NMPNs by using DMPO as spin-trapping agents for detecting •OH. h DFT calculation of catalytic reaction on metallic Pt of PtNCs. i DFT calculation of catalytic reaction on oxidized Pt of PtNCs. j, k The proposed mechanism of NMPNs to catalyze H2O2 and O2 into •OH and •O2−. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.