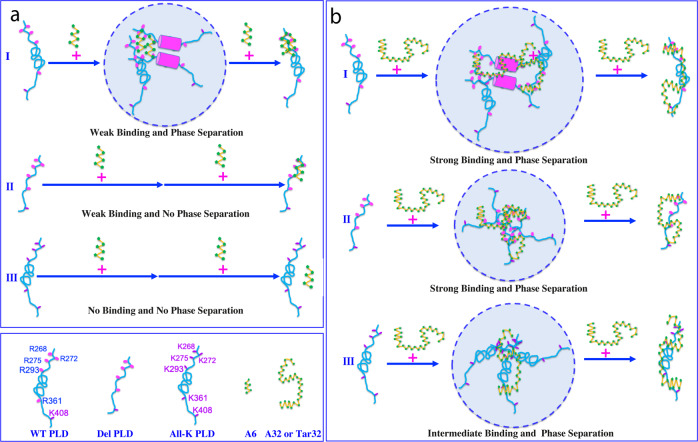
Fig. 5. Speculative mechanisms for three ssDNAs to three PLDs to modulate LLPS.
a Interactions of A6 to three PLDs. (I) For WT-PLD, A6 multivalently binds its clustered Arg268, Arg272, and Arg275 of several WR-PLD molecules to form large and dynamic A6-PLD complexes manifesting as liquid-like droplets, which is coupled with the intrinsic driving force via the oligomerization-induced formation of helices (purple cylinder) over the hydrophobic region. However, with further addition of an exceeding amount A6, LLPS is disrupted. (II) For Del-PLD, A6 is still able to multivalently bind its clustered Arg268, Arg272, and Arg275 but is no longer able to drive LLPS due to the deletion of the hydrophobic region. (III) For AllK-PLD, A6 is no longer able to tightly bind its residues as well as unable to drive LLPS due to the low binding affinity of Lys residues with nucleic acids. b Interactions of Tar32/A32 to three PLDs. (I) For WT-PLD, Tar32/A32 multivalently binds not only the clustered Arg268, Arg272, and Arg275, but also Arg293, Arg361, and Lys408 to form large and dynamic Tar32/A32–PLD complexes manifesting as liquid-like droplets, which is coupled with the intrinsic driving force via the oligomerization-induced formation of helices (purple cylinder) over the hydrophobic region. With the further addition of an exceeding amount Tar32/A32, LLPS is disrupted. (II) For Del-PLD, the multivalent binding of Tar32/A32 to the clustered Arg268, Arg272, and Arg275, as well as Arg293, Arg361, and Lys408 are sufficient to form large and dynamic Tar32/A32–PLD complexes manifesting as liquid-like droplets despite the lack of the intrinsic driving force. With the further addition of an exceeding amount Tar32/A32, LLPS is disrupted. (III) For AllK-PLD, the multivalent binding of Tar32/A32 to Lys268, Lys272, and Lys275, as well as Lys293, Lys361, and Lys408 are sufficient to form large and dynamic Tar32/A32–PLD complexes manifesting as liquid-like droplets despite the low binding affinity of Lys residues with nucleic acids. With the further addition of an exceeding amount Tar32/A32, LLPS is disrupted.