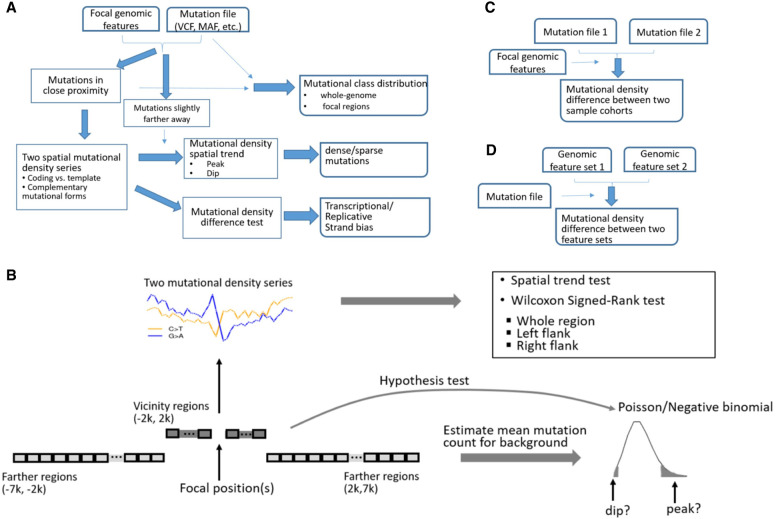
Figure 1.
Schema of MutDens. (A) The primary analysis modality entails input of one mutation file and one focal position set. Mutation counts are summarized within close proximity of focal positions (foreground) and over farther flanking regions (background). The foreground mutational counts are converted into two paired spatial mutation density series. MutDens returns three major outputs, elucidating mutational class balance, mutation spatial trend, and mutation density difference. (B) Core modules of MutDens to compare mutation density levels and to detect mutation density spatial patterns. The immediate flanking regions (defaulted to 2 kb in either direction) are sliced into continuous bins (default size, 100 bp); bin-wise mutation counts are converted to mutation density values. A trend test is conducted to detect the existence of a nonrandom spatial trend in the mutation density series. To compare the mutation density levels, a Wilcoxon test is performed between the two complementary mutational forms, in the left, right, and whole flanking region. To detect prominent mutation density spatial patterns, a null Poisson or negative binomial distribution of mutational count per bin is established based on bin-wise mutation counts from background regions (default distal/proximate boundaries, 7 kb and 2 kb). (C) MutDens can compare two sample cohorts on one set of focal positions. (D) MutDens can compare two sets of focal positions for one sample cohort.