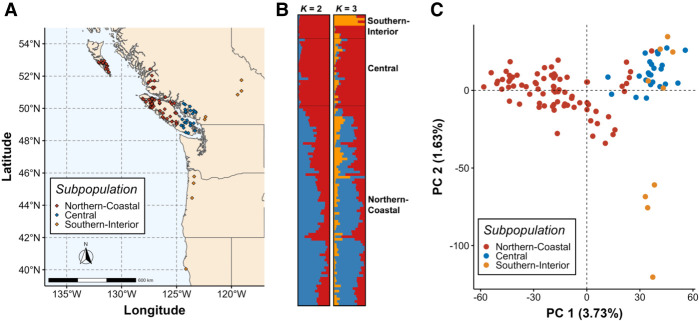
Figure 1.
Genetic structure is weak across the geographic range of western redcedar (WRC). (A) Map of geographic origin for trees in the range-wide population (RWP; n = 112). Subpopulations were defined a priori based on analysis outcomes of O'Connell et al. (2008). Trees were separated into three main subpopulations: Northern-Coastal (n = 77), Central (n = 26), and Southern-Interior (n = 9). (B) STRUCTURE plot of the RWP for K = 2 and K = 3. Optimal K was determined by evaluating STRUCTURE results using the methods of Evanno et al. (2005) and Puechmaille (2016), and by the approach of fastStructure (Raj et al. 2014). Gene flow is present throughout all three subpopulations. (C) Principal component analysis (PCA) of genetic distance between trees in the RWP. Latitudinal separation of trees from different subpopulations can be observed, although each principal component only explains a very small proportion of the variation between individuals, indicating that genetic differentiation is low.