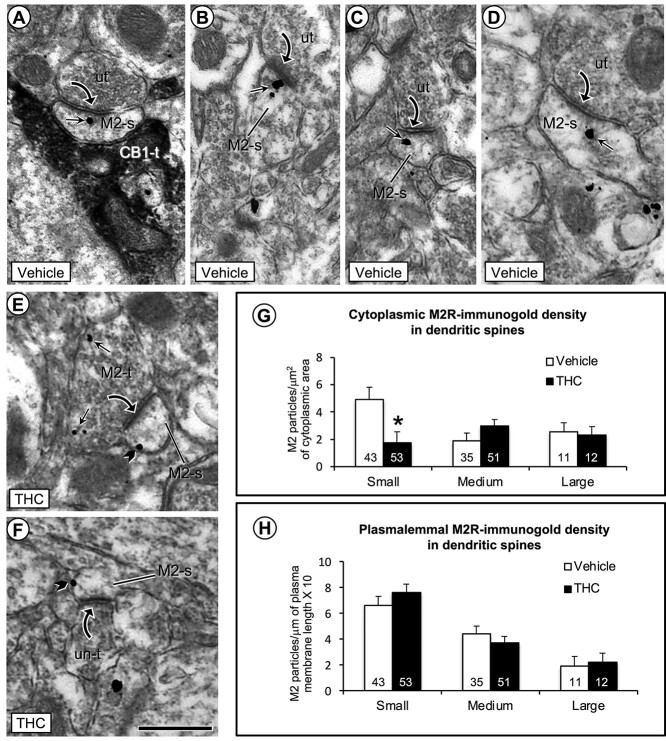
Fig. 4.
Electron microscopic images (a–f) and bar graphs (g and h) showing a significant decrease in cytoplasmic and a nonsignificant increase in plasmalemmal density of M2R immunogold in small dendritic spines in the PL-PFC of THC compared with vehicle-injected mice. a) One M2R-immunogold particle is located within the cytoplasm of a small dendritic spine that receives an asymmetric synapse from an unlabeled axon terminal and an appositional contact from an axon terminal containing immunoperoxidase labeling for CB1R (CB1-t). b–d) In vehicle-injected mice, the M2R-immunogold particles in dendritic spines without contact from CB1R-labeled terminals are seen in the cytoplasm near or more distant to the postsynaptic membrane specialization at asymmetric synapses formed by unlabeled axon terminals. e and f) In THC-injected mice, M2R immunogold particles are less commonly seen in the cytoplasm and often located on lateral portions of the plasma membrane distant from asymmetric synapses in small dendritic spines. Small straight arrows and black block arrows respectively indicate cytoplasmic and plasmalemmal M2R-immunogold particles in varying sizes of dendritic spines (M2-s). Black curved arrow = asymmetric synapse from unlabeled terminals (ut) or M2R-labeled terminals to M2R-labeled dendritic spines. g and h) Bar graphs show a significant decrease in cytoplasmic and small, but nonsignificant increase in plasmalemmal M2R-immunogold particles in small dendritic spines of the THC compared to vehicle pretreated mice. Numbers inside the bars in G-H depict absolute numbers of M2R-immunolabeled spines for each category. Asterisk = significant differences P < 0.05 ANOVA. Scale bar = 500 nm.