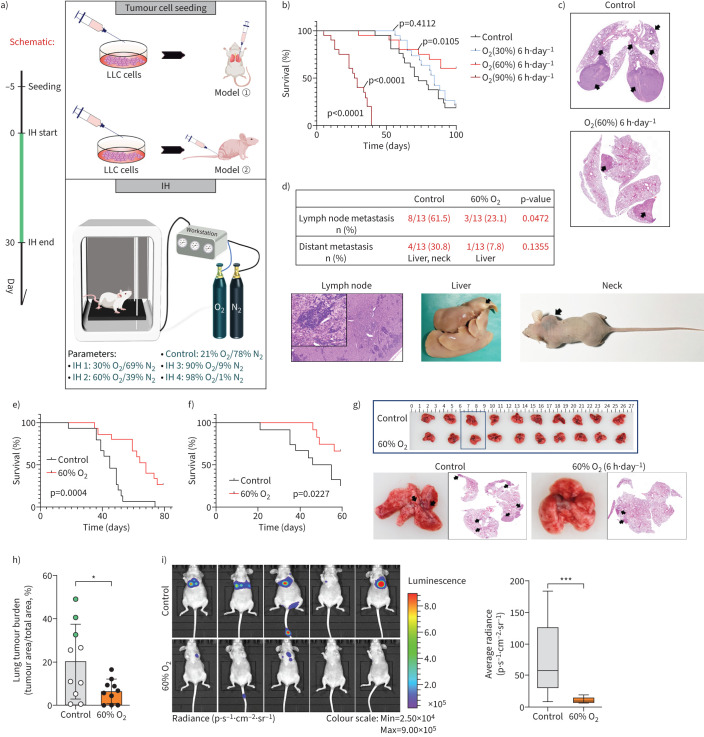
FIGURE 1.
Inspiratory hyperoxia (IH) suppresses lung cancer metastasis. a) Schematic of the workflow for the establishment of lung cancer models and IH treatment. b) Effects of IH treatment (30% oxygen (O2), 60% O2, 90% O2) on long-term survival in the orthotopic lung tumour models (n=15). Statistical significance was calculated using a log-rank test. c) Representative lung sections; arrows indicate lung tumours. d) Percentage of mice with lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis and representative images; Chi-squared test. e) 60% O2 treatment leads to long-term survival in the lung metastasis models with Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells intravenous injection (n=15); log-rank test. f) 60% O2 treatment leads to long-term survival in the lung metastasis models with H1299 cells i.v. injection (n=15); log-rank test. g) Representative lung photos and lung sections of tumour-bearing mice. h) IH decreases lung tumour burden in mice 4 weeks after i.v. injection of H1299 cells (n=10); green dot indicates mice with distant metastasis. i) Bioluminescence imaging 4 weeks after injection into mice via tail vein and box plot (n=5). *: p<0.05, ***: p<0.001 versus the indicated group, two-tailed t-test.