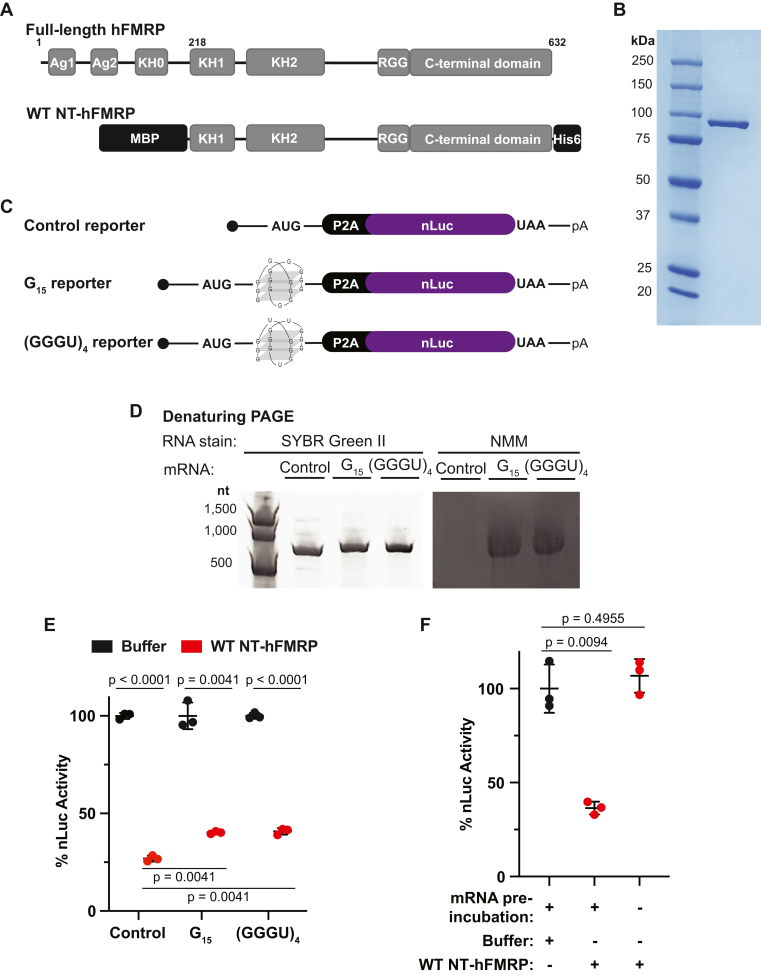
Figure 1.
FMRP inhibits translation independent of mRNA G-quadruplexes in the CDS.A, schematic of full-length (residues 1–632) and MBP- and His6-tagged WT N-terminally truncated human FMRP isoform 1 (NT-hFMRP). The Agenet 1 (Ag1), Agenet 2 (Ag2), and KH0 domains are absent in WT NT-hFRMP. Ag1 and Ag2 are also referred to as Tudor domains in some previous literature. WT NT-hFRMP harbors residues 218 to 632 of full-length human FMRP isoform 1. B, Coomassie stain of recombinant WT NT-hFMRP. C, schematic of custom nLuc reporters either lacking a G4 (control reporter) or harboring a G4 in the coding sequence (G15 and (GGGU)4 reporters). A P2A ribosome skipping motif was included immediately upstream of the nLuc coding sequence to ensure equal nLuc function between reporters. D, denaturing PAGE of control, G15, and (GGGU)4 reporters stained for total RNA with SYBR Green II or for G4 structures with NMM. E, in vitro translation of control, G15, and (GGGU)4 reporter mRNA preincubated with protein buffer or 1 μM WT NT-hFMRP. Data are shown as mean ± SD. n = 3 biological replicates. Comparisons were made using a two-tailed unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. F, in vitro translation of control nLuc reporter mRNA with protein storage buffer as a negative control, with 1 μM WT NT-hFMRP and nLuc mRNA preincubated together and with 1 μM WT NT-hFMRP without a preincubation step. Data are shown as mean ± SD. n = 3 biological replicates. Comparisons were made using a two-tailed unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. CDS, coding sequence; KH, K homology.