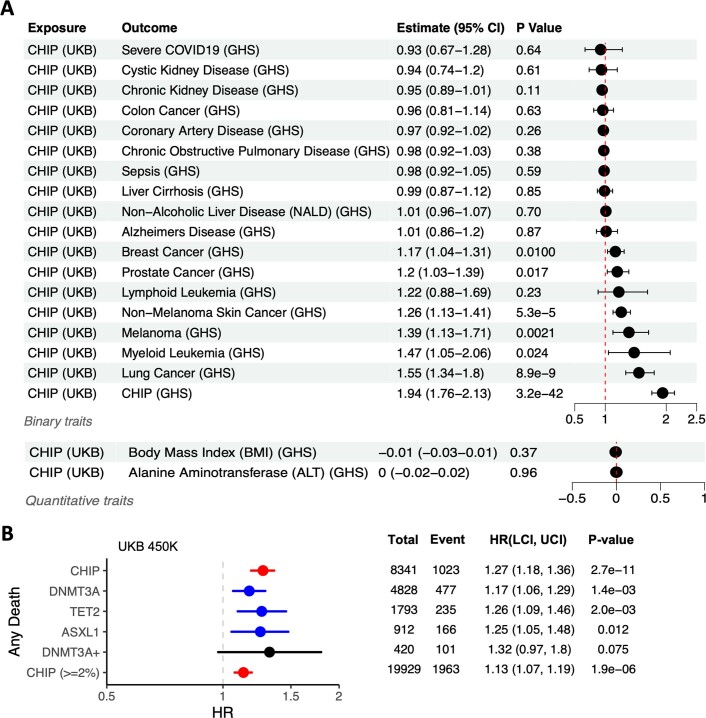
Extended Data Fig. 6. Results from Mendelian Randomization models and incident risk of death among CHIP carriers.
A. Forest plot of results from Two Sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) modeling of the effect of CHIP on 20 traits of interest (including the two quantitative traits BMI and ALT). Reported p-values are uncorrected, and reflect two-sided Z-tests derived from an inverse variance weighted (IVW) MR procedure. Significant causal association between CHIP and breast cancer, prostate cancer, non-melanoma skin cancer, melanoma, myeloid leukemia, and lung cancer are supported by these models. As expected, estimates of germline effect on CHIP from UKB and GHS are strongly correlated (odds ratio = 1.94 [1.76–2.13], P = 3.2 x 10−42). B. CHIP and its most common subtypes are significantly associated with death from any cause across UKB. Hazard ratio (HR) estimates from cox-proportional hazard models are shown, with error bars that represent a 95% confidence interval. P-values are uncorrected and derive from two-sided Wald tests. Models are adjusted for sex, LDL, HDL, pack years, smoking status, BMI, essential primary hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and 10 European specific genetic PCs.