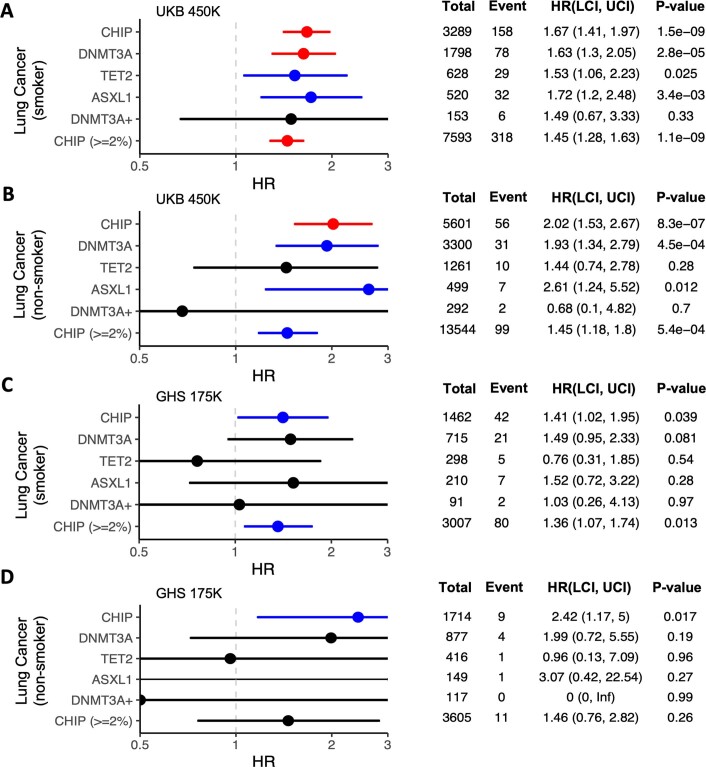
Extended Data Fig. 9. Incident risk of lung cancer among CHIP carriers from the UKB and GHS cohorts.
A-D. Forest plots and tables featuring hazard ratio (HR) estimates from cox-proportional hazard models are shown, with error bars that represent a 95% confidence interval. CHIP and its most common subtypes are significantly associated with lung cancer in both smokers and non-smokers across UKB (A-B) and GHS (C-D). Here, results are depicted from analyses in which we removed samples that had a diagnosis of malignant cancer prior to DNA collection. Models are adjusted for sex, LDL, HDL, pack years, smoking status, BMI, essential primary hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and 10 European specific genetic PCs. Hazard ratios (HR) were estimated using cox-proportional hazard modeling, with p-values uncorrected and derived from two-sided Wald tests.