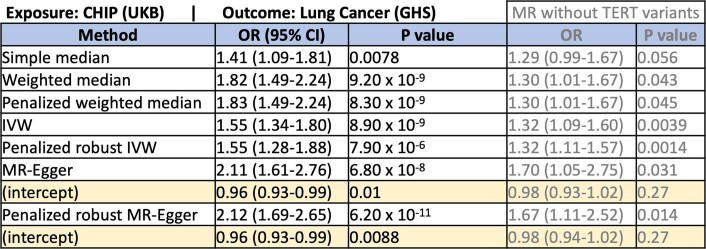
Extended Data Table 1.
Results from Mendelian Randomization analysis of CHIP exposure on lung cancer risk
Statistical results are shown from seven MR methods with differing sensitivities to outliers and/or violations of the MR assumptions. P-values are reported uncorrected. The estimated intercept values are shown for the two MR-Egger-based methods that estimate these terms. All models provided support for a casual association between CHIP and lung cancer. Models were significant when run without variants at the TERT locus as instrumental variables, which provides support for a causal association above and beyond any pleiotropic effects at the TERT locus (grey text).