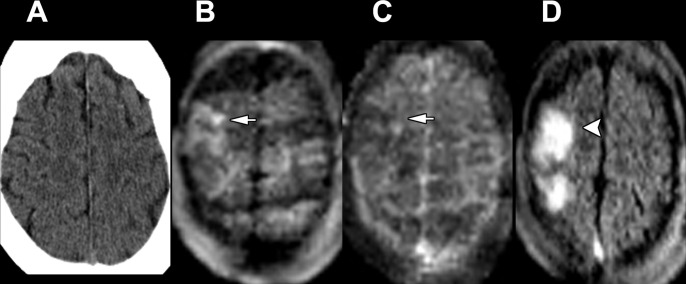
Figure 3:
Images in a 74-year-old woman admitted for left-sided weakness and right gaze preference. (A) Axial head CT scan without contrast shows no significant abnormality. (B–D) Point-of-care brain MRI scans without contrast obtained in the axial plane 2 days later with (B) diffusion-weighted imaging, (C) apparent diffusion coefficient imaging, and (D) T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging show a right middle cerebral artery territory acute infarction with restricted diffusion (arrows) and associated T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery signal abnormality (arrowhead).