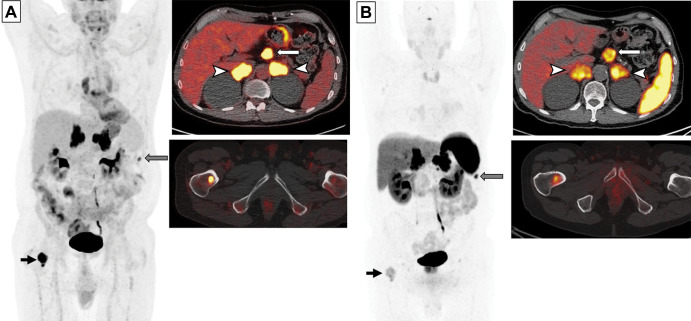
Figure 11:
Images in a 65-year-old man with small cell lung cancer who was previously treated with carboplatin and etoposide and radiation therapy to the brain and thoracic lymph nodes. The patient presented with progression of disease. (A) Whole-body fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET image (left) and fused axial FDG PET/CT scans (right) show intense FDG uptake in the bilateral adrenal lesions (arrowheads) and upper abdominal lymphadenopathy (white arrow), a peritoneal nodule (gray arrow), and a right femoral bone lesion (black arrow). FDG uptake in the bilateral paramediastinal region corresponds to the postradiation change. (B) Gallium 68 tetraazacyclododecane tetraacetic acid–octreotate (DOTATATE) whole-body PET scan (left) and fused axial PET/CT scans (right) obtained 17 days after FDG PET/CT show intense radiotracer uptake (ie, greater than the uptake in the liver) in the adrenal lesions (arrowheads) and upper abdominal lymph nodes (white arrow), a peritoneal nodule (gray arrow), and moderate radiotracer uptake (ie, similar to the uptake in the liver) in the bone (black arrow). Note a lack of DOTATATE uptake in the mediastinum in the areas of postradiation inflammatory changes, indicating high specificity of DOTATATE PET/CT for tumors compared with FDG PET/CT.