Figure 2.
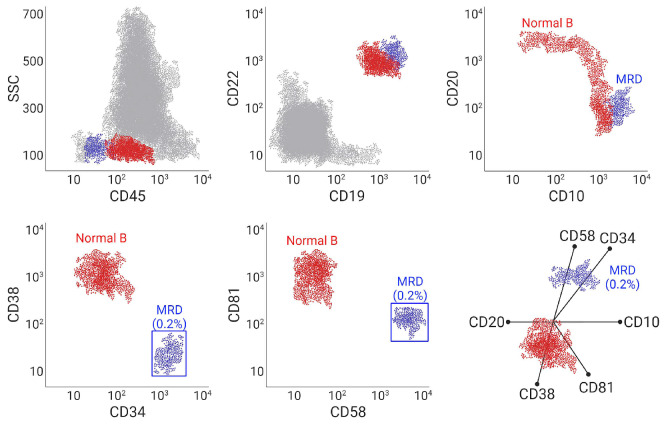
Multicolor flow cytometry as a method of measurable residual disease detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. An example showing multicolor flow cytometry of a bone marrow specimen, obtained after induction with chemotherapy plus rituximab (anti-CD20) in a patient with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). The measurable residual disease (MRD) population (0.2% of total events) is shown in blue, and distinguished from normal B cells and hematogones by its overexpression of CD10, CD58, and CD34, and underexpression of CD38 and CD81. CD20 expression is lost in leukemic blasts as a result of rituximab therapy. The radar plot visualization easily distinguishes the B-ALL MRD population.