Fig. 2.
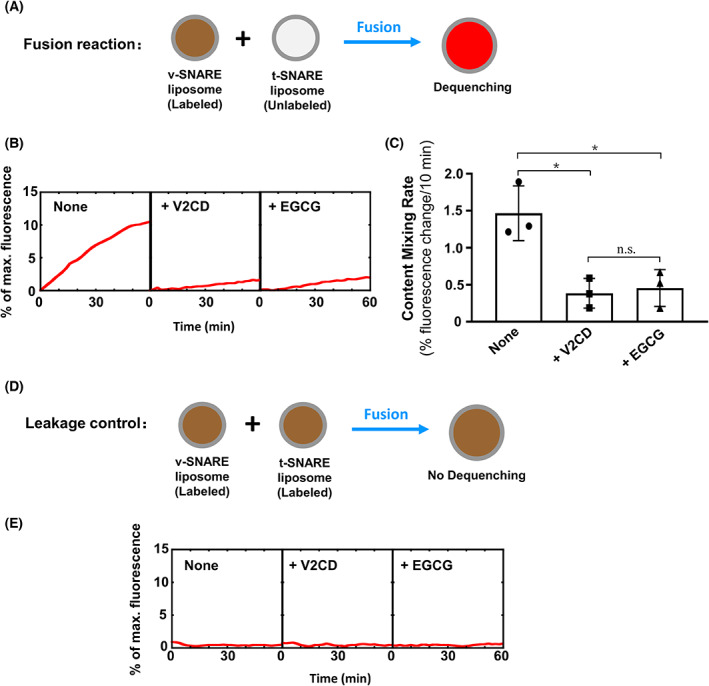
Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the content mixing of SNARE‐mediated membrane fusion. (A) Diagram of the liposome‐liposome content mixing assay. The soluble dye sulforhodamine B (50 mm) was encapsulated in the v‐SNARE liposomes, in which its fluorescence was inhibited by self‐quenching. Fusion of the v‐SNARE liposomes with unlabeled t‐SNARE liposomes led to the dequenching of fluorescence. (B) Content mixing of the reconstituted fusion reactions. The v‐SNARE liposomes were directed to fuse with t‐SNARE liposomes in the absence or presence of 10 μm EGCG. Each fusion reaction contained 5 μm t‐SNAREs and 1.5 μm v‐SNARE. Data are presented as the fluorescence increase over time. In negative controls, 20 μm V2CD was added to the fusion reactions. (C) Initial content mixing rates of the fusion reactions shown in (B). Data are presented as a percentage of fluorescence change per 10 min. Error bars indicate the SD. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3 independent replicates). P values were calculated using ordinary one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. n.s., P > 0.05; *P < 0.05. (D) Diagram of the leakage control reactions. Sulforhodamine B was included in both v‐ and t‐SNARE liposomes. (E) The leakage controls of the content mixing reactions. Increases in sulforhodamine B fluorescence were not observed, indicating that no detectable content leakage occurred during the fusion reactions.
