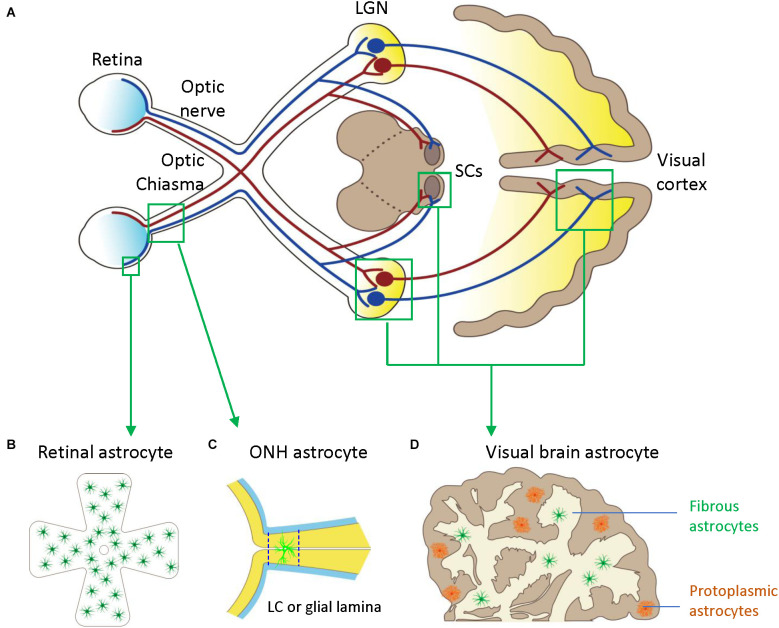
Figure 1.
Astrocytes in the visual pathway may be related to the pathogenesis of glaucoma. (A) The schematic diagram showing the visual pathway, including retina, optic nerve, optic chiasma, LGN, SCs, and visual cortex. (B) Retinal astrocytes mainly reside in the nerve fiber layer (NFL) and orient in a monolayer surrounding RGC axons and blood vessels. (C) Optic nerve head (ONH) astrocyte processes are oriented perpendicularly to RGC axons, separating them into bundles. The two dash lines label the position of LC (human) or glia lamina (rat or mouse). (D) Visual brain astrocytes in LGN, SCs, and visual cortex, have two types including protoplasmic astrocytes of gray matter and fibrous astrocytes of white matter. LGN, lateral geniculate nucleus; LC, lamina cribrosa; NFL, the nerve fiber layer; ONH, optic nerve head; RGC, retinal ganglion cells; SCs, superior colliculi.