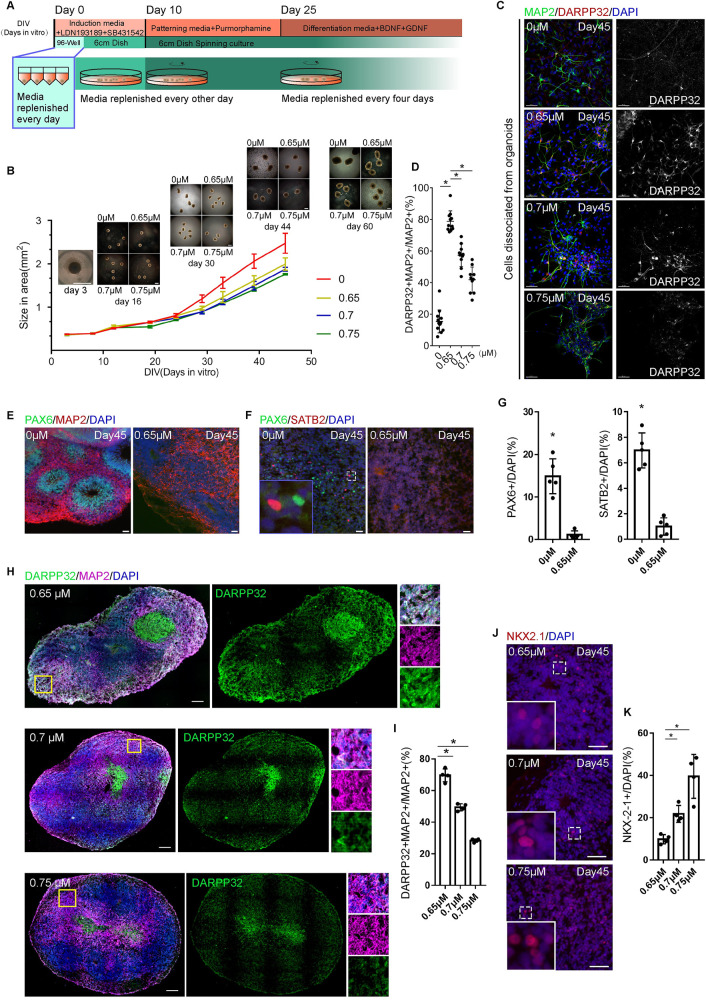
Fig 1. Generating human striatal organoids.
(A) The schematic of brain organoid protocol with a ventral drug-patterning application (purmorphamine) during culture. (B) The morphology of organoids with different concentrations of ventral drug-patterning applications in culture. Scale bar, 1 mm. Quantification of organoid size from Day 0 to Day 44 in cultured (mean ± SD, n = 4 organoids). (C, D) Immunostaining and quantifying DARPP32 and MAP2 antibodies revealed the effects of Pur in striatal-fate patterning in dissociated neurons from organoids (n = 6 organoids). Data, mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA. *, P < 0.05. Scale bar, 50 μm. (E–G) Immunostaining for PAX6, SATB2, and MAP2 antibodies revealed dorsal and ventral fates distinguished by Pur addition to organoids after Day 45 in culture. Scale bar, 50 μm. Quantifying the expression levels of PAX6 and SATB2 in sections after 45 days in culture. Organoids, n = 5. Data, mean ± SD. Student t test. *, P < 0.05. (H, I) Immunostaining and quantification for DARPP32 and MAP2 antibodies revealed that the decreased striatal fates with increasing Pur in Day 45 organoids (n = 4 organoids). Data, mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA. *, P < 0.05. Scale bar, 50 μm. (J, K) Immunostaining and quantification for NKX2.1 antibody revealed that the patterned fates shifted from LGE to MGE, increasing Pur on Day 45 (n = 4 organoids). Data, mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA. *, P < 0.05. Scale bar, 50 μm. The raw data underlying this figure can be found in the S1 Data. LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; MGE, medial ganglionic eminence.