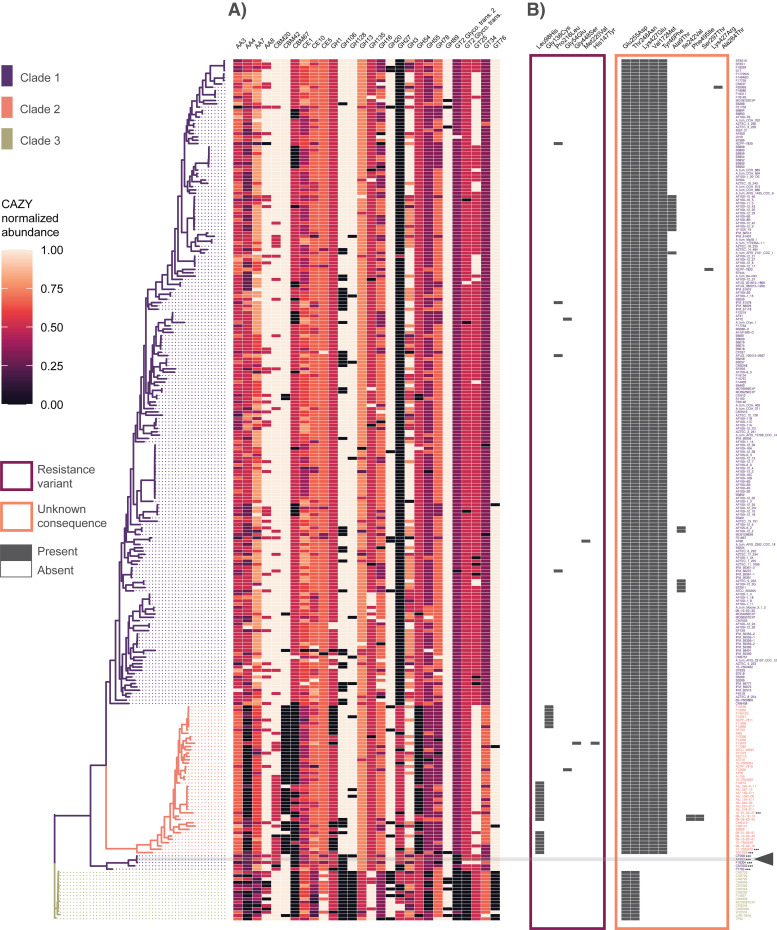
Fig 6. Distribution of CAZymes and occurrence of cyp51A mutations across the A. fumigatus phylogeny.
(A) CAZyme profiles display patterns of both clade-specific gene gains and clade-specific gene absences across 28 CAZyme classes. CAZyme classes with differential abundance between the 3 clades were determined by Kruskal–Wallis tests at p < 0.001 after Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons. Gene counts are normalized on a 0–1 scale (by CAZyme class) for visualization. (B) Identification of non-synonymous variants in the cyp51A gene across the phylogeny demonstrated structured occurrence of both known resistance variants (framed in pink) and variants with unknown functional impacts (framed in orange). Reference strain Af293 is highlighted in gray and with triangle. While the Leu98His variants (corresponding to the azole resistant TR34/Leu98His genotype) as well as azole resistant variant Gly138Cys were found exclusively in Clade 2, other characterized variants were scattered in low abundance throughout Clade 1, 2, or both. No characterized resistance variants were found in Clade 3. While some non-synonymous variants with unknown functional impacts occurred frequently in cyp51A and represented changes in a single branch leading to the reference strain Af293 (Glu255Asp, Thr248Asn), others were absent form this branch and absent in Clade 3 (Lys427Glu, Val172Met, Tyr46Phe), while others were low abundance and exclusive to Clade 1 (Ala9Thr, Lys427Arg, Ile242Val, Ala284Thr), or Clade 2 (Ser297Thr, Phe495Ile). The data underlying this figure can be found in DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.5775265.