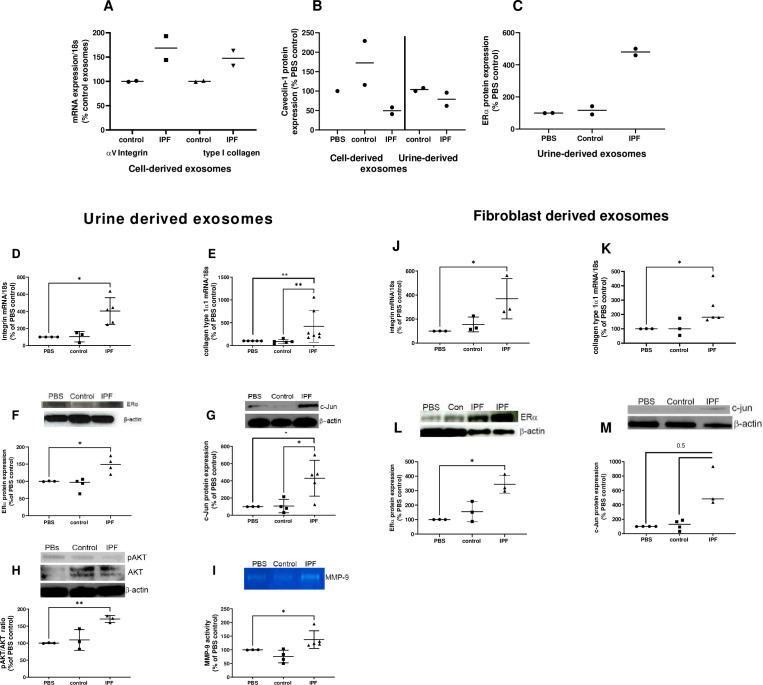
Figure 7. Fibrotic pathways are activated in lung punches after injection with urine (U-IPFexo) or myofibroblast-derived (MF-IPFexo) exosomes.
Human (A–C) and mouse lung (D–M) punches were injected with PBS alone, U-IPFexo (D–I) or MF-IPFexo (J–M) or age and sex-matched control urine exosomes or lung fibroblast exosomes from control subjects (without lung disease). Punches were collected 4 days later and processed as described in Methods. Human lung punches were injected with MF-IPFexo or fibroblast cell derived exosomes (panels A and B) or urine-derived control exosomes and U-IPFexo (panels B and C). n=2 human lung punch isolates, 2 biological exosome preparations/group. Panels D-M, n=3 mouse lung replicates/group, n=3–5 biological exosome isolates/group Data are graphed as percent PBS control. αv-integrin (panels A, D and J, Figure 7—source data 1) and collagen type 1 (panels A, E and K, Figure 7—source data 1) mRNA expression increased in punches injected with IPFexo (derived from urine or myofibroblasts). Downstream fibrotic pathways; ERα (C, F and L), activated AKT (H), c-Jun (G and M), protein expression and MMP-9 activity (I) were also stimulated by exosomes from individuals with IPF. * p<0.05, **p<0.01. p Values were calculated by Mann Whitney U test.