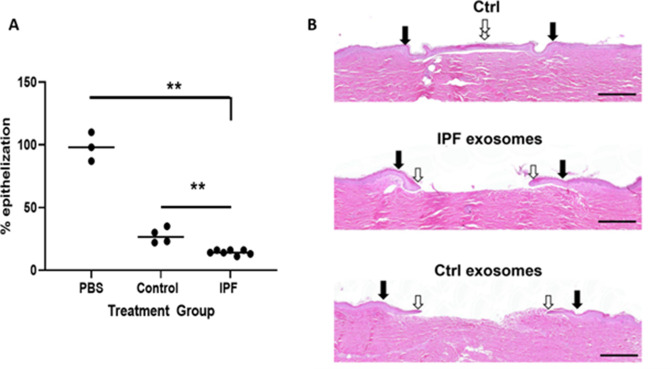
Figure 8. Epithelization in ex vivo wound healing is decreased by urine-derived IPF exosomes (U-IPFexo).
Human skin was wounded, injected with U-IPFexo or control (age and sex-matched from individuals without lung disease) exosomes and maintained at the air-liquid interface. Wound healing was assessed at day 4 post-wounding, a time point when exponential epithelialization occurs. (A) Data are graphed as mean with each data point representing a single wound. Experiments were performed using triplicate technical replicates and two to three biological replicates (Figure 7—source data 1). p<0.005 PBS and control compared to IPF, PBS vs control = 0.05 p values were calculated by Mann Whitney U test. (B). Photos of gross skin show visual signs of closure and correspond to the histology assessments. Black arrows point to the initial site of wounding, while white arrows point to the wound edge of the migrating epithelial tongue. Scale bars, 500 µm proportional to the image size.