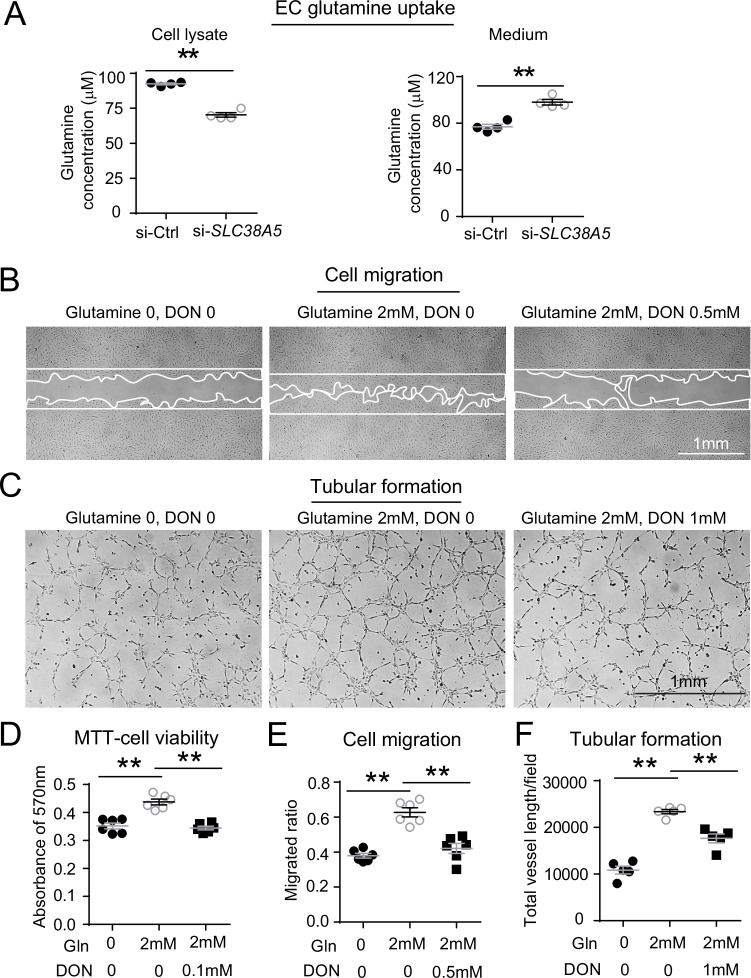
Figure 6. SLC38A5 facilitates endothelial cell (EC) uptake of glutamine, which is essential for EC viability, migration, and tubular formation.
(A) SLC38A5 knockdown with si-SLC38A5 suppressed glutamine uptake by human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMECs), with decreased glutamine levels in HRMEC cell lysates and increased culture medium levels, measured with a glutamine/glutamate-Glo bioluminescent assay. Levels of glutamine/glutamate in HRMECs and culture medium samples were determined from bioluminescence readings by comparison to a standard titration curve. (B & E) HRMECs were grown to confluence, and a scratch was applied to generate a wound. Mitomycin was used to stop cell proliferation. A glutamine antagonist, 6-diazo-5-oxo-norleucine (DON), was used to broadly inhibit glutamine uptake. 16 hr were given to the cells to migrate. Representative images are shown in (B), and the quantification of migrated areas is shown in (E). (C, F) HRMECs treated were seeded onto Matrigel for 9 hr and treated with glutamine and DON for tubular formation. Representative images are shown in (C), and the quantification of total vessel length per field is shown in (F). (D) HRMEC cell viability was measured at 24 hr by MTT assay and normalized to the levels at 0 hr to quantify the cell growth rate. Scale bars: 1 mm (B&C). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n=4–6 per group. *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01.