Fig. 1. Depletion of MIF-1 but not MIF-2, or both MIF-1&2 in female mice with severe acute EAE resulted in significantly reduced clinical scores. Additionally, all groups, especially MIF-1-KO mice, were treated successfully with DRα1-MOG-35-55.
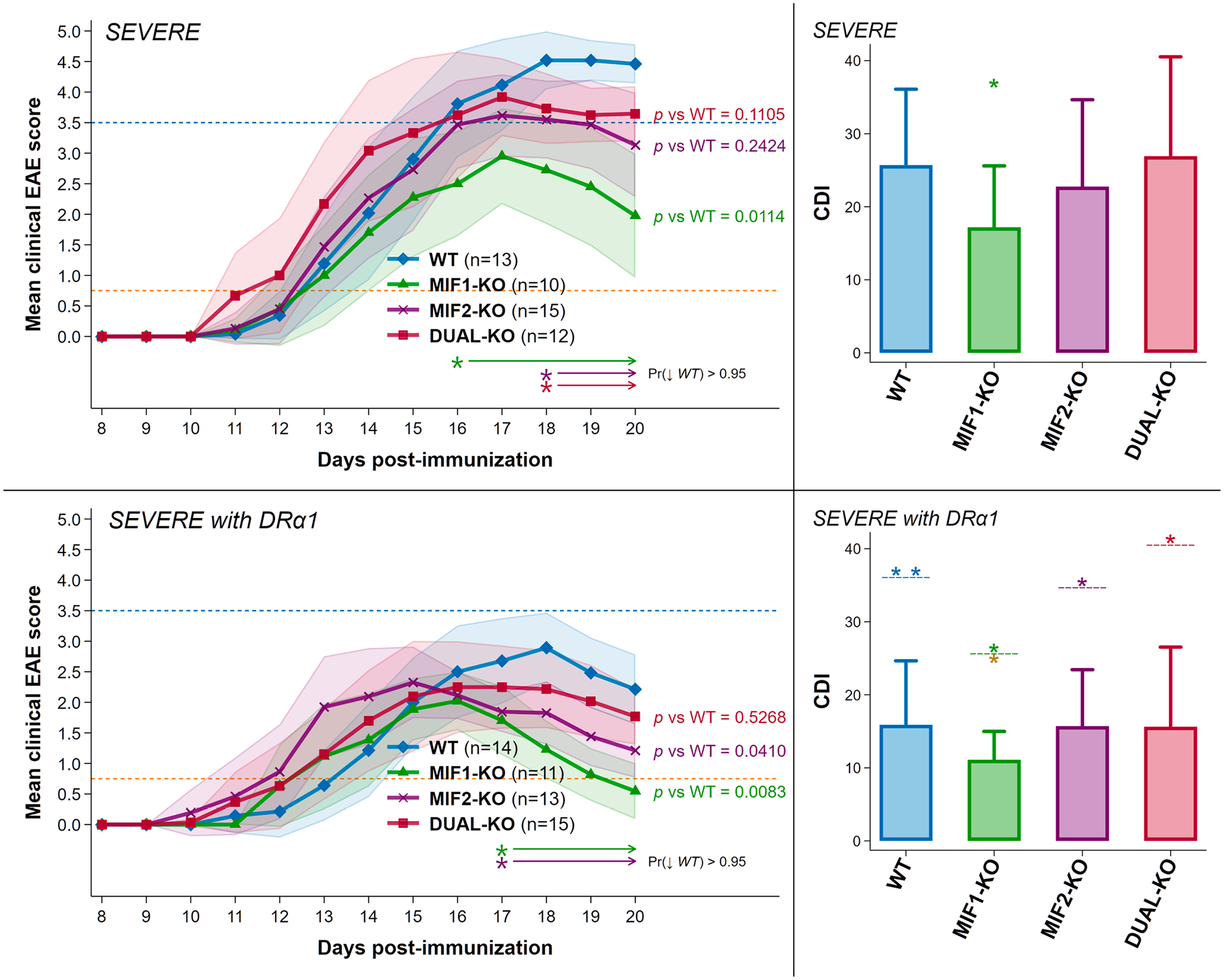
Upper Panels: Depletion of MIF-1 significantly reduced the mean final daily EAE score from 4.5 in WT to 2.0 in MIF-1-KO mice and the cumulative disease index (CDI) score from 26 in WT mice to 17 in MIF-1-KO mice with nominal changes in MIF-2-KO and DUAL-KO mice. Lower panels: Treatment of severe EAE with 5 daily doses of 100 μg DRα1-MOG-35-55 further reduced mean final daily scores for all groups to average (and even maximum) scores < 3.0 and for MIF-1-KO mice to ~ 0.75 (see blue and orange reference lines at EAE scores of 3.5 and 0.75) and EAE CDI scores (WT = 16; MIF-1-KO = 11; MIF-2-KO = 16; DUAL-KO = 16). The matched-color arrow-tipped lines underneath each set of curves [Pr (↓WT)] indicate spans of time where the joint probability that the corresponding curves lie strictly below the WT curve for all indicated spans exceeds 95% according to a Bayesian calculation based on noninformative reference priors. In CDI plots: *p ≤ 0.05 **p ≤ 0.01 for CDI scores in all WT vs. non-WT; and in all DRα1-mMOG-35-55 vs. group-coded Vehicle-treated groups (above dashed line); and for DRα1-MOG-35-55-treated MIF-1-KO mice vs. all other treated groups (below dashed line for MIF-1-KO CDI).
