Fig. 2.
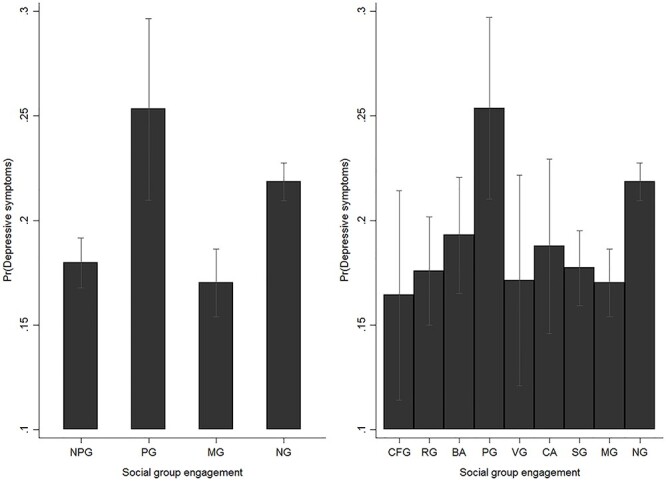
The effects of social group engagement on the probability of depression among older adults, by types, Taiwan, 1996–2007. Note: NPG: non-political groups, PG: political groups, MG: multiple groups, NG: no groups, CFG: community friendship groups, RG: religious groups, BA: business associations, VG: volunteer groups, CA: clan associations, SG: senior groups. All results were based on random-effects panel logit models. Results correspond to model 1 and 2 of Table S3, supplementary material. Source: the author.
